As COVID-19 pushes the AIDS response even further off track and the 2020 targets are missed, UNAIDS is urging countries to learn from the lessons of underinvesting in health and to step up global action to end AIDS and other pandemics
GENEVA, 26 November 2020—In a new report, Prevailing against pandemics by putting people at the centre, UNAIDS is calling on countries to make far greater investments in global pandemic responses and adopt a new set of bold, ambitious but achievable HIV targets. If those targets are met, the world will be back on track to ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030.
The global AIDS response was off track before the COVID-19 pandemic hit, but the rapid spread of the coronavirus has created additional setbacks. Modelling of the pandemic’s long-term impact on the HIV response shows that there could be an estimated 123 000 to 293 000 additional new HIV infections and 69 000 to 148 000 additional AIDS-related deaths between 2020 and 2022.
“The collective failure to invest sufficiently in comprehensive, rights-based, people-centred HIV responses has come at a terrible price,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “Implementing just the most politically palatable programmes will not turn the tide against COVID-19 or end AIDS. To get the global response back on track will require putting people first and tackling the inequalities on which epidemics thrive.”
New targets for getting back on track
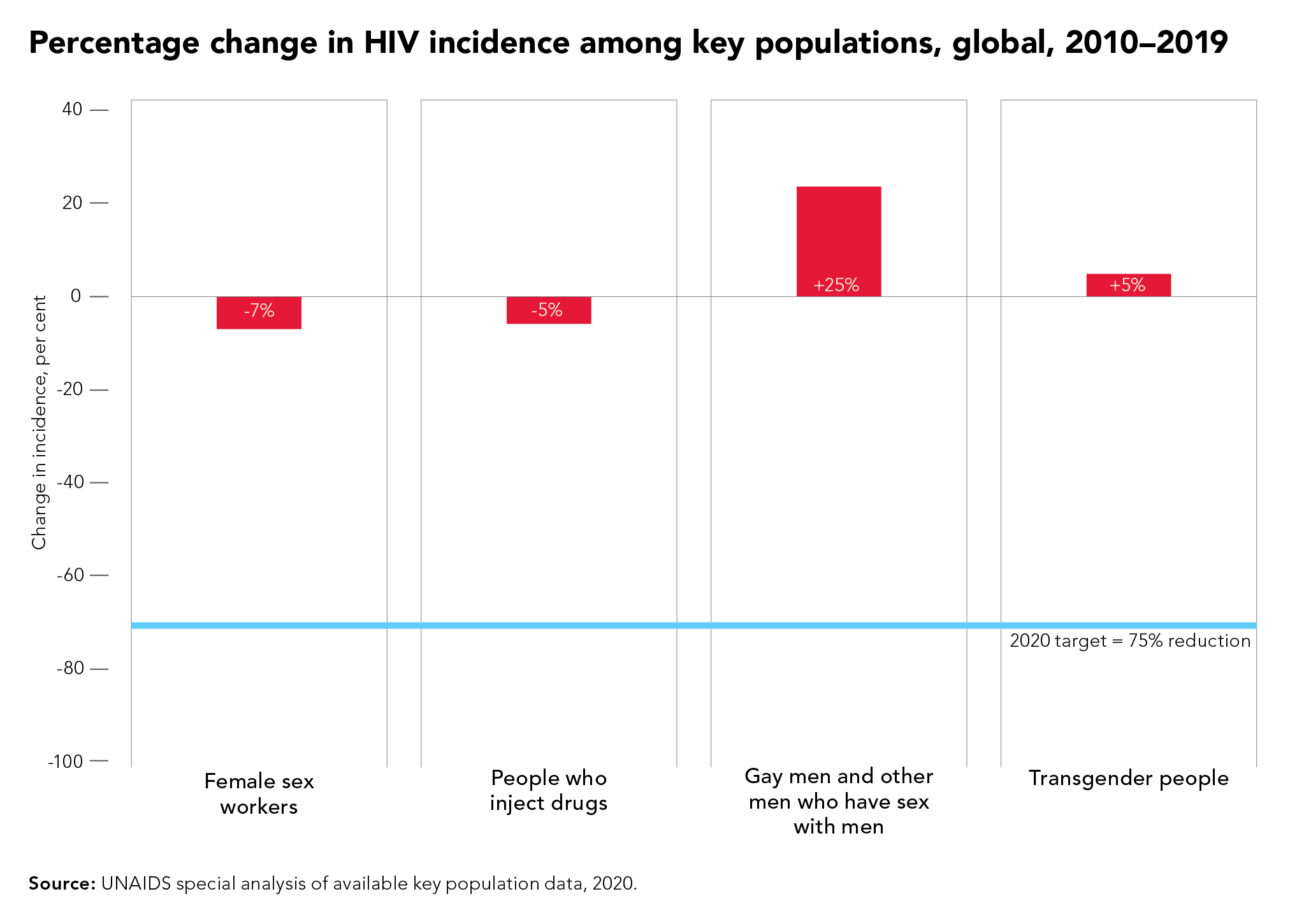
Although some countries in sub-Saharan Africa, such as Botswana and Eswatini, have done remarkably well and have achieved or even exceeded the targets set for 2020, many more countries are falling way behind. The high-performing countries have created a path for others to follow. UNAIDS has worked with its partners to distil those lessons into a set of proposed targets for 2025 that take a people-centred approach.
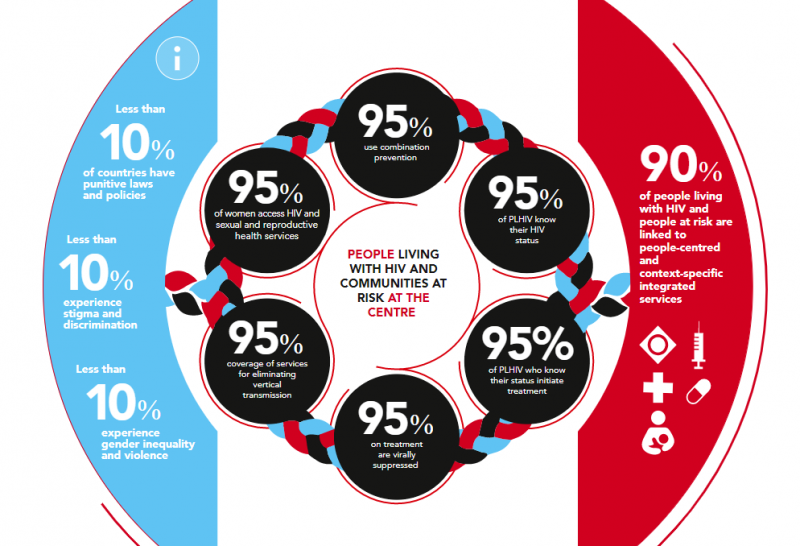
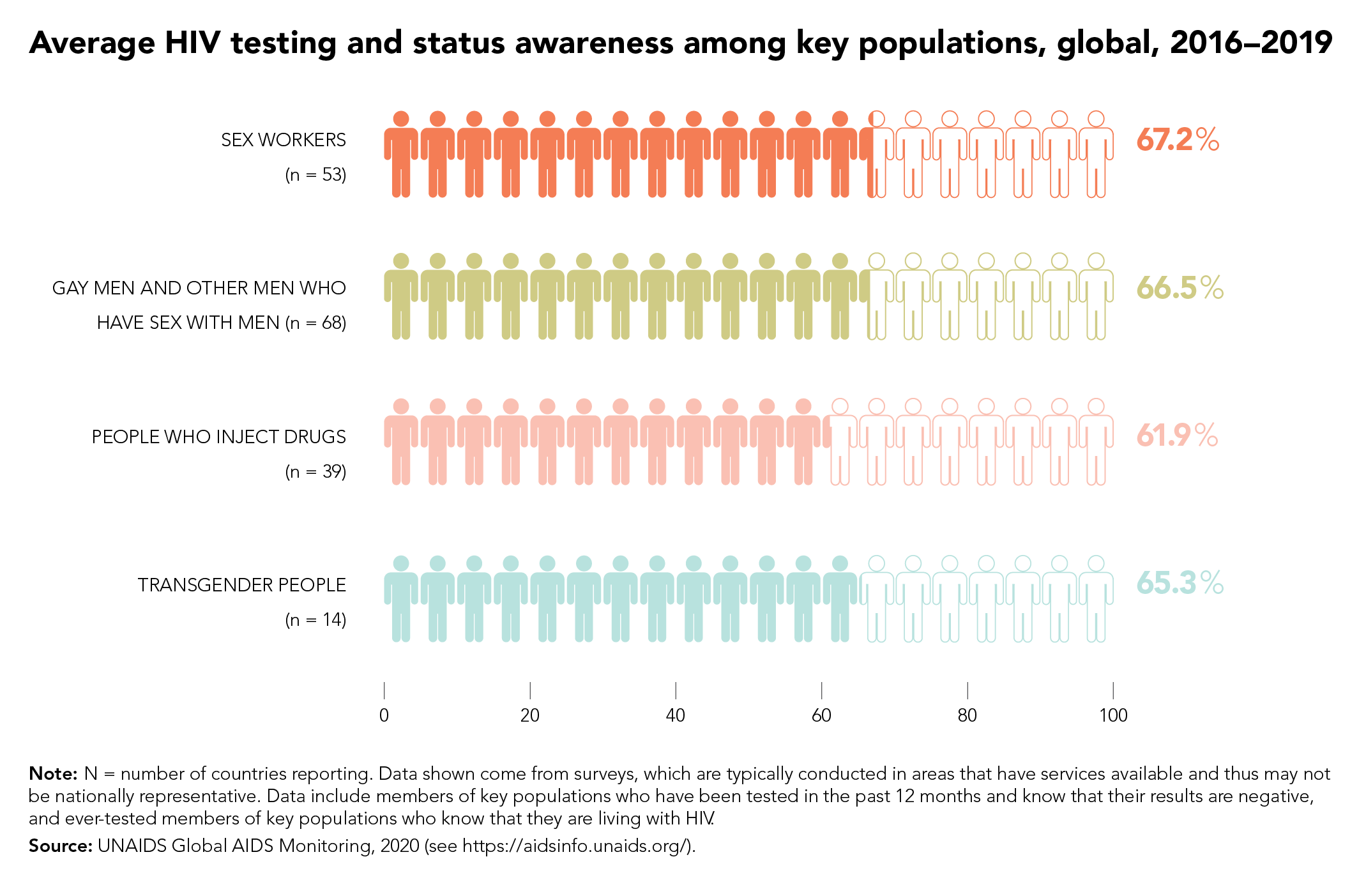
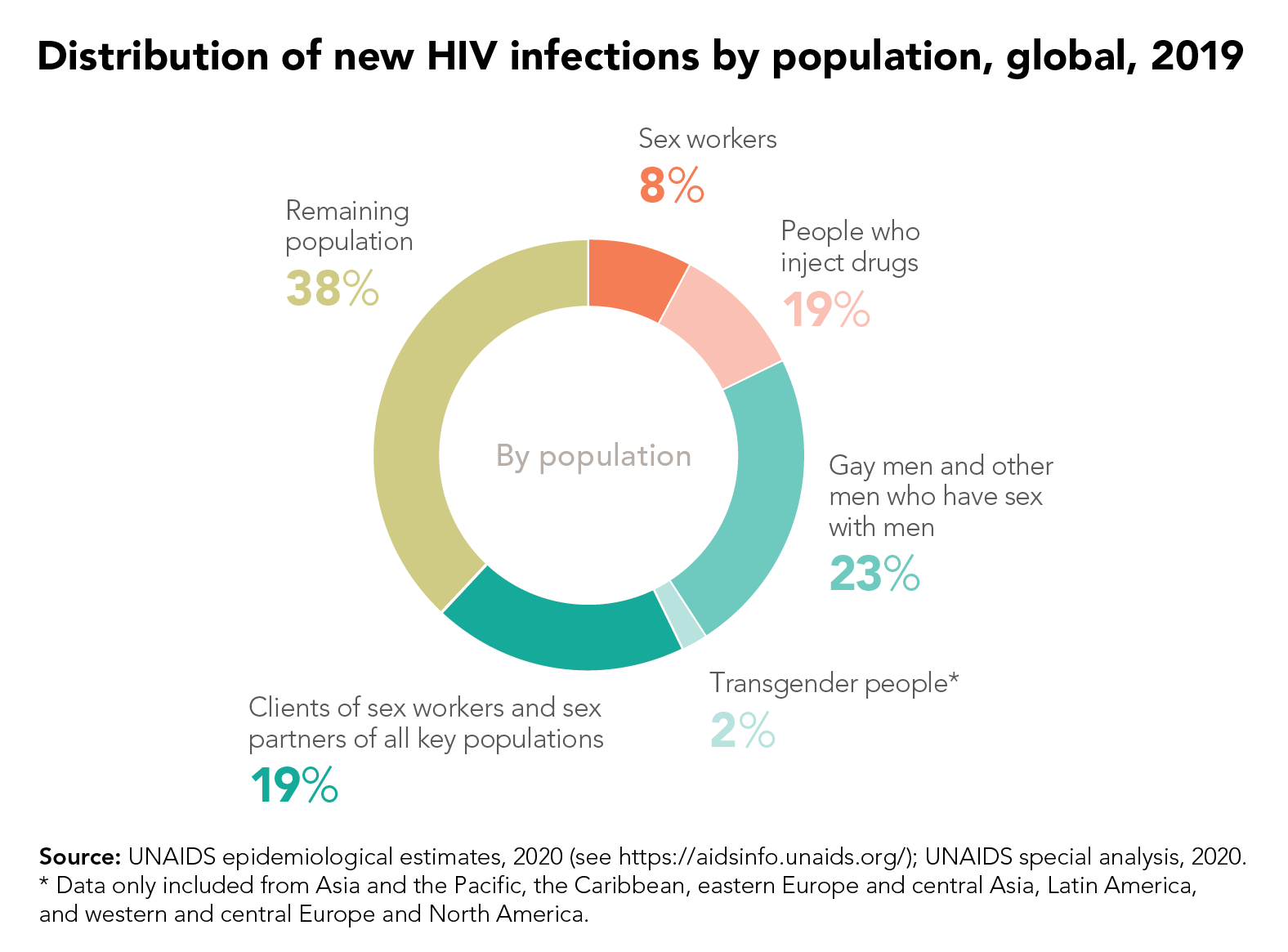
The targets focus on a high coverage of HIV and reproductive and sexual health services together with the removal of punitive laws and policies and on reducing stigma and discrimination. They put people at the centre, especially the people most at risk and the marginalized—young women and girls, adolescents, sex workers, transgender people, people who inject drugs and gay men and other men who have sex with men.
New HIV service delivery targets aim at achieving a 95% coverage for each sub-population of people living with and at increased risk of HIV. By taking a person-centred approach and focusing on the hotspots, countries will be better placed to control their epidemics.
The 2025 targets also require ensuring a conducive environment for an effective HIV response and include ambitious antidiscrimination targets so that less than 10% of countries have punitive laws and policies, less than 10% of people living with and affected by HIV experience stigma and discrimination and less than 10% experience gender inequality and violence.
Prevailing against pandemics
Insufficient investment and action on HIV and other pandemics left the world exposed to COVID-19. Had health systems and social safety nets been even stronger, the world would have been better positioned to slow the spread of COVID-19 and withstand its impact. COVID-19 has shown that investments in health save lives but also provide a foundation for strong economies. Health and HIV programmes must be fully funded, both in times of plenty and in times of economic crisis.
“No country can defeat these pandemics on its own,” said Ms Byanyima. “A challenge of this magnitude can only be defeated by forging global solidarity, accepting a shared responsibility and mobilizing a response that leaves no one behind. We can do this by sharing the load and working together.”
There are bright spots: the leadership, infrastructure and lessons of the HIV response are being leveraged to fight COVID-19. The HIV response has helped to ensure the continuity of services in the face of extraordinary challenges. The response by communities against COVID-19 has shown what can be achieved by working together.
In addition, the world must learn from the mistakes of the HIV response, when millions in developing countries died waiting for treatment. Even today, more than 12 million people still do not have access to HIV treatment and 1.7 million people became infected with HIV in 2019 because they did not have access to essential HIV services.
Everyone has a right to health, which is why UNAIDS has been a leading advocate for a People’s Vaccine against COVID-19. Promising COVID-19 vaccines are emerging, but we must ensure that they are not the privilege of the rich. Therefore, UNAIDS and partners are calling on pharmaceutical companies to openly share their technology and know-how and to wave their intellectual property rights so that the world can produce successful vaccines at the huge scale and speed required to protect everyone.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.