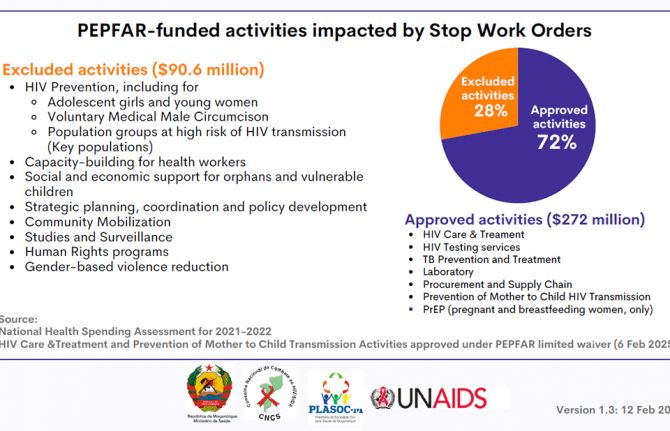
Feature Story
Survey shows that the COVID-19 pandemic increases vulnerability of LGBTI people
10 July 2020
10 July 2020 10 July 2020The opening session of the 2020 International AIDS Conference shared the findings of a rapid online survey demonstrating the increased socioeconomic vulnerability of lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex (LGBTI) people due to COVID-19.
UNAIDS, the LGBT+ Foundation and researchers from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and other universities around the globe convened a COVID-19 disparities working group. It surveyed more than 20 000 LGBTI people in 138 countries in April and May and found that three quarters (74%) were fully or partially locked down, leading to economic consequences for many.
About 13% of the survey participants have already lost their jobs in the wake of the pandemic and a fifth (21%) are expecting to lose it in the near future. Nearly half the survey participants (47%) faced economic difficulty, with a quarter unable to meet their basic needs, skipping meals or reducing meal sizes.
Of concern, 21% of participants living with HIV reported that they had experienced “interrupted or restricted access” to refills of antiretroviral therapy and 42% of those said they had less than a month’s supply on hand. Worrisome disruptions were also reported for pre-exposure prophylaxis and access to HIV testing. The study also highlights that racial and ethnic minorities consistently have lower access to HIV services.
Erik Lamontagne, Senior Economist at UNAIDS and one of the members of the working group, reported at the conference that the crisis had pushed 1% of respondents to start engaging in sex work and that 2% had to continue to sell sex during the COVID-19 pandemic, risking exposure to the coronavirus. The pandemic has reduced the ability to negotiate safer sex for 13% of respondents, potentially increasing their risk of acquiring HIV. Respondents also reported reduced access to safe injecting equipment and opioid substitution therapy.
“What worries us is that socioeconomic factors, such as limited access to health care, lower income, unemployment and food insecurity, combined with higher anxiety and depression rates, may place some at higher risk of contracting HIV and affect treatment adherence among people living with HIV,” said Mr Lamontagne.
The study shows that COVID-19 increases the vulnerability of groups that are already disproportionately affected by HIV. Solutions and targeted programmes are required from the global community and governments to sustain prevention, testing and treatment services and to help the LGBTI community not only to survive but emerge from the crisis.