



Feature Story
South Africa charts a new frontier by rolling out a twice-yearly injection which is almost 100% effective in preventing HIV
24 October 2025
24 October 2025 24 October 2025South Africa has taken a decisive step towards stopping new HIV infections. The South African National AIDS Council (SANAC) and the National Department of Health, in collaboration with UNAIDS, convened a two-day national meeting on access to a new, and potentially groundbreaking medicine (lenacapavir) which is set to be rolled out in South Africa in early 2026.
Minister of Health Dr Aaron Motsoaledi affirmed government’s commitment to make lenacapavir “a public good - accessible, affordable and locally produced”. He emphasised the importance of prioritising adolescent girls and young women. There are around 8 million people living with HIV in South Africa and every week around 1000 adolescent girls and young women become newly infected with HIV.
“The introduction of lenacapavir marks the beginning of a new phase in HIV prevention, one grounded in collaboration between government, communities, our partners like the Global Fund and UNAIDS and the private sector,” said Dr Motsoaledi. “This partnership must be accountable, transparent and inclusive if we are to achieve our national targets.”
South Africa is among nine countries globally selected to roll out the medicine under the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, TB and Malaria’s financial commitment to reach 2 million people across low- and middle-income countries.
“Science continues to offer us new tools, but innovation alone is not enough,” said Eva Kiwango, UNAIDS Country Director for South Africa. “Equity must follow. Communities, especially young women and key populations, have waited too long for HIV prevention they can trust and use with dignity.”
Through a US$ 29 million grant, South Africa will receive enough medicine to provide HIV prevention to 450 000 people at high risk of HIV during a rollout in 23 high-incidence districts across six provinces. The aim is to reach adolescent girls, young women, sex workers, men who have sex with men, people who use drugs and other at risk populations.
“We are not gathered merely to discuss a medicine, but to reaffirm our collective commitment to justice and equality,” said Steve Letsike, Deputy Minister for Women, Youth and People living with Disabilities. “No young woman, no queer person, no person with a disability must be left behind in the promise of HIV prevention.”
Across both days, a common message resonated: partnership is South Africa’s greatest strength. Dr Thembisile Xulu, SANAC CEO, called for unity of purpose noting, “We must move from conversation to coordination, and from coordination to action.”
Yvette Raphael, Co-founder of the Advocacy for Prevention of HIV and AIDS in South Africa emphasised the need to take the message to communities, saying, “Civil society must be given the tools for demand creation to provide research literacy in the way that we and communities understand.”
The evidence and the promise
Presenting findings from the PURPOSE 1 and 2 trials, Professor Linda-Gail Bekker, CEO of the Desmond Tutu Health Foundation reported 100 % efficacy among cisgender women and 96% efficacy among men, transgender and non-binary participants. She highlighted that long-acting prevention tools such as lenacapavir expand choice, strengthen agency, and promote equity, offering new hope to those who need discreet and durable protection.
Professor Helen Rees, from WITS RHI, emphasised the issue of misinformation and disinformation as South Africa prepares to roll out lenacapavir next year. She said that all stakeholders, “Must underscore the importance of science because if there is mistrust in science, people will not trust new products. As we roll out lenacapavir we must have our ears on the ground for misinformation and disinformation.”
Gilead Sciences, developer of lenacapavir, represented by Country Manager, Wendy Cupido affirmed its commitment to ongoing dialogue and partnership with the Government of South Africa and stakeholders to ensure affordable, equitable access. She noted that the manufacturer of lenacapavir Gilead remains ready to engage with the country and partners as they explore local manufacturing readiness.
Speaking during a panel discussion, young Shout Out Now ambassador, Lerato explained the impact of missing one day of oral PrEP means putting yourself at risk of acquiring HIV. She said, “I am looking forward to lenacapavir to reduce my monthly visits to the clinic to access medication and all the relevant screenings to keep myself safe from HIV. It will make my life easier.”
Dr Yogan Pillay, Director HIV and TB delivery at the Gates Foundation underlined how collaboration is transforming affordability. Recent landmark agreements secured by Unitaid, CHAI, Wits RHI and Gates will make generic lenacapavir available at a cost of US$ 40 a year in 120 low- and middle-income countries starting in 2027. “Sustainability isn’t imported -it’s built,” he said, noting the importance of local manufacturing and data-driven delivery.
The meeting entitled Lenacapavir Access and Sustainability was held in Johannesburg on 14 and 15 October, 2025. Over 100 participants participated in person and 130 joined virtually. The consultation marked the launch of the rollout of Lenacapavir in South Africa which is set to start in 2026.
Region/country
Documents
Consultation on the Projected Impact and Cost-Effectiveness of Long-Acting Injectable Lenacapavir as Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis
06 June 2025
Documents
What can modelling tell us about the scale-up of lenacapavir for pre-exposure prophylaxis?
18 September 2025
Scaling up primary HIV prevention, including pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP), is essential to closing the prevention gap and reducing the number of new HIV infections, especially as countries approach the 95–95–95 treatment targets1 but continue to face a stagnant or rising incidence of HIV among people from key and priority populations. Injectable lenacapavir is a new long-acting injectable antiretroviral medicine given every six months for HIV prevention. In clinical trials, lenacapavir was found to be safe and effective, with 96–100% reduction in HIV acquisition compared with background rates.


Feature Story
Lower prices needed for new HIV prevention medicine in Brazil
09 September 2025
09 September 2025 09 September 2025Civil society representatives are demanding an urgent price reduction for long-acting injectable HIV medicines which prevent HIV.
During a public hearing at the Chamber of Deputies in Brazil, representatives called for strategies to expand access to innovative injectable HIV medications, including lenacapavir and cabotegravir, which have demonstrated more than 95% efficacy in preventing HIV infection.
The discussion was organized by The Committee on Human Rights, Minorities, and Racial Equality and brought together representatives of pharmaceutical companies, the government, and civil society.
“We are talking about rights,” stated Congresswoman Erika Kokay. “It is not a consumer relationship, it is a relationship of human rights and health that allows the population to take ownership of their own research. We are talking about a country where more than 10,000 people die every year due to AIDS-related illnesses.”
Despite Brazil being one of the countries which participated in the lenacapavir clinical trials (together with Argentina, Mexico, and Peru) it has been excluded from the list of countries that have received a licence to produce its generic version.
“Brazil was excluded from the licence because it is considered a middle-income country, which does not reflect the intense inequalities that exist in Brazil,” pointed out Susana Van der Ploeg, coordinator of Working Group on Intellectual Property. “In 2022, 23% of new HIV infections occurred in countries that were excluded from the licence, including countries that participated in clinical studies,” she added.
According to UNAIDS, Latin America is one of three regions in the world where the annual number of new HIV infections has increased, representing 13% of all new HIV infections between 2010 and 2024.
“When an innovation can save people’s lives but does not reach the people who need it, can we really consider it an innovation?” said Luciana de Melo, HIV/AIDS Coordinator at the Ministry of Health. “Price is a key issue in the incorporation of medicines to the country’s health system”
Cabotegravir, registered by ViiV Healthcare, is an injection administered once every two months to prevent HIV. The drug was approved by the Brazilian Health Surveillance Agency (ANVISA) in 2023 and launched on the Brazilian private market in August 2025. Currently, its average cost is R$ 4,000 per dose (U$ 740), around 2,5 times the minimum wage in Brazil. According to Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics, 31.8% of the population lived on an income between one and three minimum wages in 2023. There is still no date for the drug to be offered through Brazilian health system.
Lenacapavir, from the pharmaceutical company Gilead, is administered once every six months and is in the process of being registered for use in HIV prevention. Gilead has not yet announced the price of the drug to be used for HIV prevention in Brazil but its cost in the United States for treatment was recorded at over US$ 28,000 per person per year.
An article published in The Lancet magazine presents a different perspective for the generic version. The study projects that the cost of generic lenacapavir could range from as low as US$ 35 to US$ 46 per person per year. In addition, growth in demand could reduce this amount to US$ 25 per person per year if there were a committed demand of five to ten million people.
“We will not be able to reach our goals if we do not view access to health as a human right,” said Andrea Boccardi Vidarte, UNAIDS Country Director, Brazil.
Watch the full hearing (in Portuguese): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bcBecwT-WzY
Watch the full hearing (in Portuguese)
Region/country
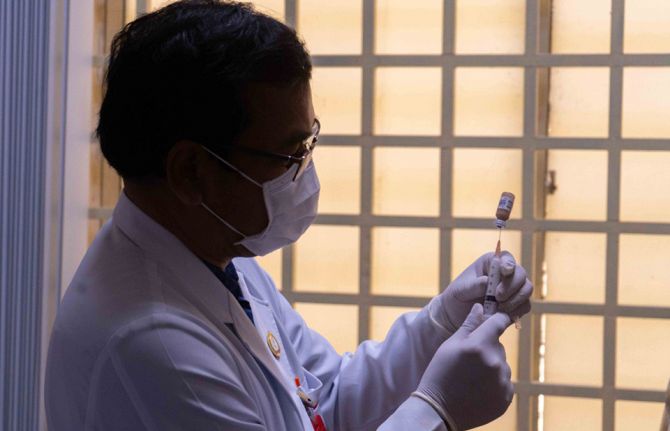
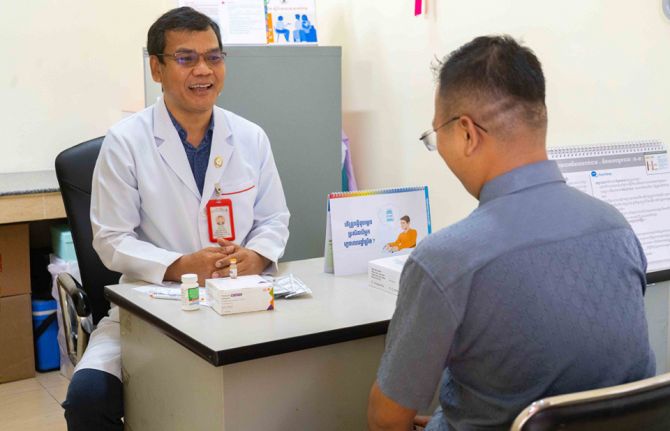



Feature Story
Cambodia becomes the second country in the Asia Pacific to offer long-acting PrEP
04 July 2025
04 July 2025 04 July 2025Borey and Sophea have both used PrEP—a medicine taken every day to avoid contracting HIV. But while this solution has worked, it was not a perfect fit.
Due to his active professional and personal life, Borey sometimes forgot to pack his pills.
“This makes it easy to miss doses, especially when I have unplanned sexual encounters,” he said.
Sophea, a female entertainment worker, is more concerned about her HIV risk with her intimate partner than at work where she uses condoms.
“I don’t fully trust that he is monogamous… he may have other partners. So, it is important for me to protect myself,” she explained.
Still, she says she’s become tired of taking a pill every day for the last six months.
Borey and Sophia are among the first clients in Cambodia to begin long-acting injectable Cabotegravir (CAB-LA), a PrEP formulation administered every two months. With this initiative, Cambodia has become a frontrunner in the Asia Pacific region to roll out long-acting PrEP.
This HIV prevention tool is aimed primarily at groups of key populations at higher risk of HIV infection including men who have sex with men, transgender women, female entertainment workers, people who inject drugs, and couples with one HIV-positive and one HIV-negative partner. This solution is being prioritized for individuals who face challenges with daily pill adherence, those with frequent risk exposure, and those who prefer a more discrete prevention method.
“Offering multiple PrEP options enhances our ability to meet the diverse needs of individuals at risk of HIV,” explained Ouk Vichea, Director of the National Center for HIV/AIDS Dermatology and STD (NCHADS). “Not everyone is comfortable with, or able to adhere, to a daily oral regimen. CAB-LA provides a long-acting alternative that can improve adherence and reduce stigma.”
Offering diverse and innovative HIV prevention solutions is a key strategy as Cambodia embarks on what it hopes is the final chapter towards ending AIDS as a public health threat. The country has made great progress, providing treatment to almost all people it diagnoses and achieving viral suppression among more than 98% of people on antiretroviral therapy.
However, HIV prevention remains a challenge. Every day three people are newly infected with HIV. Nine of every ten new infections occur among people from key population communities (88%). Almost half of new infections (44%) are among young people while 79% are among men.
As a young, gay man, Borey is aware of the risks and welcomes a solution he considers to be more user-friendly.
“With CAB-LA, I don’t have to worry about remembering to take a pill every day. It gives me peace of mind and helps me stay prepared and protected. It fits well with my lifestyle because I have multiple partners and don’t always feel trust. CAB-LA makes things easier, especially in situations where sex is unplanned,” he said.
NCHADS ensures that counseling is client-centered and focuses on providing clear, non-judgmental information about all available PrEP options.
“We discuss the benefits, potential side effects, dosing schedules, and how each option fits into the client’s lifestyle. We also assess their risk profile, preferences, and any barriers they may face. The goal is to support informed decision-making and ensure clients feel confident and comfortable with their choice,” Mr Ouk said.
Patricia Ongpin, UNAIDS Country Director to Cambodia, Lao PDR and Malaysia stressed the importance of choice.
“We should present people with options and ask what fits their lives. When we pair people with suitable prevention solutions, they are more likely to be consistent,” she said.
NCHADS is exploring several innovative approaches to strengthen HIV prevention. One key development is the upcoming launch of the dapivirine vaginal ring-PrEP (DVR-PrEP). This will offer women a long-acting prevention method they can control. Cambodia will be the first country in the region to make this option available.
In addition, the clinic will expand the use of digital tools for adherence support, and community-led delivery models to increase accessibility and trust. They continue to monitor advancements in next-generation PrEP products, including future injectable and implantable options, to ensure the most effective and client-centered prevention tools are available to the people who need them most.
Region/country

Press Release
UNAIDS urges Gilead to drop price of new HIV prevention shot
18 June 2025 18 June 2025GENEVA, 18 June 2025—The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved long-acting injectable lenacapavir for HIV prevention. The new medicine is administered by injection once every 6 months and is a significant step in improving prevention options for people at risk of HIV infection around the world. In an interview with the New York Times, Gilead Sciences has announced a US list price of $28,218 USD per person per year.
In a research paper published in The Lancet HIV this week, experts found that generic lenacapavir could cost $35-$46 per person-year. This could fall to $25 per person-year for a committed demand of five to ten million people within the first year, bringing pricing in line with or lower than current oral PrEP.
Responding to news of Lenacapavir’s FDA approval, Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS and United Nations Undersecretary-General, said:
“This is a breakthrough moment. The approval of lenacapavir is a testament to decades of public investment, scientific excellence, and the contributions of trial participants and communities. I congratulate Gilead and US partners for advancing this important innovation. Lenacapavir could be the tool we need to bring new infections under control – but only if it is priced affordably and made available to everyone who could benefit.
“UNAIDS has seen research that lenacapavir can be produced for just $40 per person per year, falling to $25 within a year of roll out. It is beyond comprehension how Gilead can justify a price of $28,218. If this game-changing medicine remains unaffordable, it will change nothing. I urge Gilead to do the right thing. Drop the price, expand production, and ensure the world has a shot at ending AIDS.”
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Documents
A shot at ending AIDS — How new long-acting medicines could revolutionize the HIV response
21 January 2025
Breakthrough innovations have come to light that have proved to be more than 95% effective in preventing HIV infection with injections just twice a year. Once a year might even be possible. They could also be key for 40 million people living with HIV around the world who need better options for treatment. It’s not a cure or a vaccine, but it could be a game-changer if made accessible to all who could benefit. Read press release More on lenacapavir: UNAIDS welcomes the announcement of new deals to make new HIV prevention medicines available and affordable for people in need | UNAIDS welcomes US announcement to expand access to medicine to prevent HIV and urges greater global ambition to reach all in need | UNAIDS calls on leaders at Davos to commit to rapid global access to revolutionary new long-acting HIV medicines | A shot at ending AIDS — How new long-acting medicines could revolutionize the HIV response


Press Release
UNAIDS calls on leaders at Davos to commit to rapid global access to revolutionary new long-acting HIV medicines
21 January 2025 21 January 2025UNAIDS urges speed and compassion urging pharmaceutical companies to enable access to new, life-saving medicines
DAVOS/GENEVA, 21 January 2025—Today, at the World Economic Forum’s annual meeting in Davos, Switzerland the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) has warned that new long-acting HIV prevention – and potentially treatment – medicines can help usher in the end of AIDS if corporate and political leaders move quickly and urgently to prioritise access for all low and middle-income countries.
Lenacapavir, produced by Gilead Sciences, has proved to be more than 95% effective in preventing HIV with just two doses a year and the company is now conducting trials of once-yearly shots. ViiV Healthcare has the injectable medicine Cabotegravir, administered once every two months to prevent HIV, which is already being used in some countries. Month-long vaginal rings are also in use and longer acting pills and vaginal rings are being trialled.
“These new technologies offer us a real shot at ending AIDS by 2030,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS and Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations. “But it comes with a caveat—only if pharmaceutical companies, governments, international partners and civil society unite around an HIV prevention and treatment revolution, can we use these medicines to their full potential and end AIDS much sooner than we previously thought.”
The breakthrough long-acting medicines could stem new HIV infections and are already being used to suppress the virus for some people living with HIV. But their potential can’t be unlocked unless everyone, everywhere who could benefit has access.
UNAIDS is urging pharmaceutical companies to move faster and ensure “affordable pricing and generic competition” in the market for the new HIV medicines. “We have no problem with profit, but we will not stand for profiteering,” said Ms Byanyima.
Gilead and ViiV have licensed generics manufacturing to a number of countries, which is to be applauded, but they are moving too slowly. Generics aren’t expected until next year- and many countries have been left out. Nearly all of Latin America, a region of rising HIV infections, has been excluded. In addition, to provide for the whole world, Gilead has licensed just six companies to make generic versions of the medicine – with no producer in sub-Saharan Africa. To make these medicines widely available and affordable, more generic production is needed.
Gilead has not announced a price for lenacapavir for prevention. However, used as treatment in the United States, the medicine can cost around US$ 40 000 per year per person. One study suggests that, if 10 million people are reached, generics could cost just $40 per person per year, a thousand times less.
At the end of 2023 only 3.5 million people are using pre-exposure prophylaxis. UNAIDS goal is to reach 10 million with preventative HIV medicine by the end of 2025. “This is possible, said Ms Byanyima, “But only if we have ambition. Look at injectable contraceptives—72 million women around the world accessed them in 2022. Look at COVID-19 vaccines in rich countries – 4.5 billion people were vaccinated in a year. Why can we not have the same ambition for HIV? We did it for HIV treatment and we can do it for prevention. We have done it before – and we can do it again.”
Today, 30 million of the 40 million people living with HIV are now on treatment—a huge, but long-awaited achievement which destroyed families and cost far too many lives.
While these new medicines are not a cure or a vaccine, they could halt the HIV pandemic.
The Global Fund to fight AIDS, TB and Malaria and the US President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) recently announced a deal to get lenacapavir to 2 million people over the next three years. Which is a good start but not ambitious enough.
"Science has delivered a miraculous new tool: medicines that prevent HIV infection with injections just twice a year and which could work for treatment too,” said Ms Byanyima. “We must do better this time. Either companies step up, or governments step in. This is our shot to end AIDS – and we cannot afford to miss it."
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Contact
UNAIDSSophie Barton-Knott
tel. +41 79 514 6896
bartonknotts@unaids.org
UNAIDS
Joe Karp-Sawey
tel. +44 74 2898 5985
karpsaweyj@unaids.org





Press Statement
Global leaders in the HIV response call for access to long-acting medicines
10 December 2024 10 December 2024NAIROBI, 10 December 2024—Today, at the 55th Programme Coordinating Board for the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS), HIV leaders from across the world called for access to long-acting medicines for everyone who would benefit from them, to build toward a new era in the AIDS response.
Over the last two years, scientific breakthroughs have brought to the fore a new class of anti-HIV medicines with long-acting effects, allowing people at risk of HIV infection and those living with the virus to take medicines every few months. One is injected just twice a year. Recent studies have shown these medicines to be among the most effective ever developed. One study showed zero new infections among young African women using long-acting prevention drugs, while a study among key populations showed them more effective than oral medicines. Another study highlighted at the session showed encouraging results using long-acting HIV treatment in low- and middle-income countries.
At the “Leadership in the AIDS Response” session at the UNAIDS board, government officials, researchers, manufacturers, and civil society called for accelerating global access to use these scientific breakthroughs to interrupt the continuing AIDS pandemic. Despite existing HIV prevention tools, in 2023 an estimated 1.3 million people newly contracted HIV – two every minute. Despite HIV treatment, there is still one AIDS-related deaths every minute.
Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS, said: “We can usher in a new era by connecting technological innovation with access for all. Let us act boldly together, bring down the curve of new infections, and dramatically accelerate the HIV response.
“Let us learn from the painful lessons of the past so that we write a new story now. In the late 1990s and early 2000s, even after antiretroviral medicines were proven to be effective and rolled out in high-income countries, 12 million people on this continent still died waiting for those drugs. We can - and must – do better with long-actings. We urge the companies producing these medicines to expand their generics licenses. And we support governments making use of all their legal flexibilities to get access to affordable medicines.
“The usual trajectory is that the Global South waits years before the science reaches them. What if we do not wait for years, what if we ensure that science is treated as the public good it is? What if we disrupt the far too slow trajectory we are on and shift to a trajectory that accelerates progress, ends the pandemic, enables sustainability, and can be a model for the world?"
Secretary Ethel Maciel, Secretary of Health of Brazil, said: “Brazil has a long history of making use of technology in the HIV response. The possibility of having new long-acting medicines in the global response is a great opportunity. But we have the huge challenge of the high cost of these medicines, and the difficulty for a range of countries, including ours, to access them.
“Brazil is committed to work together in the fight to ensure that this new technology is made available to all people all over the world who are at risk of and living with HIV.”
Dr Cissy Kityo, Executive Director of the Joint Clinical Research Centre, Uganda, a leading scientist working on trials of long-acting medicines said: “We have these fantastic new tools. The technology of long-acting ARV’s antiretrovirals is remarkable. The evidence is now clear that long acting medicines will be game-changers for both prevention and treatment. The science is in, the question is how well we will use it.”
Mr Javier Padilla Bernáldez, Secretary of State for Health, Spain, said: “This new long-acting technology puts us in an exceptional situation, not an ordinary one, an opportunity that we cannot afford to miss. Long-acting medicines can change the landscape of the HIV response. But if this game-changing innovation did not reach the people it would be a nothing-changer!
“We need to remember the 2000s’ fight for universal access. We cannot repeat the same mistakes and delays of before. We need to ensure that no countries should be pressured if they choose to use the safeguards in the TRIPS agreement. The inequality gap is a global problem. We need a universal perspective, so that all countries, including middle-income countries, are included.”
Dr Sylvia Vito, Africa Head of EVA Pharma, a company in Egypt licensed to produce a generic version of lenacapavir, said: “We are a company that will not sit comfortably, but rather be in a good hurry to support the unmet HIV medical needs for our people. We intend to move fast on product development, production, and eventual registration. It is our intention that high quality long-acting generic ARV medicine will not only be available, but made accessible and affordable as well. We intend to beat the current standard of care in HIV treatment and prevention by going further to improve on the current options for patients in low and middle-income countries.”
The importance of generic production was central to the interventions of speakers. Several speakers noted the obstacle that much of Latin America, a region of rising HIV infections, has been excluded from companies’ voluntary licenses for generic versions. This is despite Brazil, Peru, Mexico and Argentina participating in clinical trials. Speakers highlighted the importance of using TRIPS flexibilities for enabling access under World Trade Organization rules, which can enable governments to supply its citizens with generic versions of patented treatments either through domestic production or imports. In the 2021 Political Declaration on HIV/AIDS, countries committed to make use of TRIPS flexibilities, specifically geared to promoting access to medicines.
Although Gilead Sciences, the producer of lenacapavir, one of the new class of long-acting medicines, has not yet announced the price of its product for use as PrEP, it costs around $40,000 per person per year in the United States where it is used for treatment. However, experts have estimated that it could be produced and sold for $40 per person per year, in line with UNAIDS estimates for sustainable pricing in low- and middle-income countries. Speakers highlighted opportunities to bring down the price of these medicines through generics, expanded local and regional production, and the use of TRIPS flexibilities by member states.
One important opportunity for progress emphasized by speakers was to build on the progress on multilateral collaboration made by Brazil, which as chair of the G20 in 2024, successfully secured worldwide support for the Global Coalition for Local and Regional Production, Innovation and Equitable Access, laying the foundations for a greatly expanded and more equitable access to medicines.
Speakers noted also the importance of choice, and of widening access to a range of new technologies, of which lenacapavir is just one. Speakers highlighted important current innovations including 2-monthly injectable cabotegravir and a three-month dapivirine vaginal ring, as well as new technologies currently in the pipeline including a once-a-month pill may move into phase 3 trials next year.
Reinforcing the importance of accelerating access to long-acting medicines, The New England Journal of Medicine has today published an article by UNAIDS Executive Director Winnie Byanyima, Linda-Gail Becker of the Desmond Tutu HIV Centre, and Matthew Kavanagh of Georgetown University’s Center for Global Health Policy and Politics, entitled “Long-Acting HIV Medicines and the Pandemic Inequality Cycle — Rethinking Access”.
The article showed that the “pandemic inequality cycle” in HIV has usually meant a decade delay between access to breakthrough HIV technologies in the global North and the global South.
In their article the authors write: “The world may look back on 2024 as a pivotal time in the fight against AIDS — the start of a revolution in the global biomedical response to HIV using long-acting antiretroviral medicines. Whether they will do so depends on whether policymakers and pharmaceutical companies avoid repeating past mistakes.”
The authors call for “a nonlinear approach to global access to ARVs that combines far more rapid sharing of technology, decentralized global production, and research and development of products that meet the needs in Africa, Asia, Latin America, and the Caribbean.”
They highlight the need for progress on long-acting treatment as well as prevention and “to break the long-standing pattern of failing to get HIV technologies to the people who need them most, to stop playing catch-up, stop accepting that innovations must reach people in the Global South years late, and use long-acting medicines to help end the pandemic.” The article is available at https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMms2412286
The importance of long-actings, and what is at stake in the discussions on access, was summed up by Jerop Limo, a 26 year old Kenyan activist born living with HIV who is Executive Director of the Ambassador for Youth and Adolescent Reproductive Health Program (AYARHEP):
“Taking a pill every day is not easy. It is a constant reminder of being different, and the stigmatising and shaming we experience because of it can discourage us from taking our medicines.
“This is not just about convenience. Young people living with HIV, and young people at risk of HIV, are clear: with all the pressures we face, long-acting medicines would help us stay on the medicines and help transform, and save, our lives.
“We deserve to live, and to live fully. We can’t have access on paper only. We need access for all people in all countries.
“I am inspired to see leaders coming together to centre communities and to call for access to long-acting HIV medicines. With partnership we can do this. We don’t have time to wait.”
The UNAIDS Programme Coordinating Board brings together governments, civil society and the United Nations to help guide the HIV response. UNAIDS sees the development of long-actings as a vital disruptive innovation.
“The arrival of long-acting injections is a game-changer which can help prevent millions of new HIV infections, if we ensure access to all who would benefit from them,” said Ms Byanyima. “Today, in Nairobi, leaders in the global HIV response took a bold and vital step forward on the path to access for all.”
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Documents
Take the rights path to end AIDS — World AIDS Day report 2024
26 November 2024
The world’s decades-long response to HIV is at an inflection point. Despite successes, the world is currently not on track to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030. Press release | Download full report | Download short version







