

Press Statement
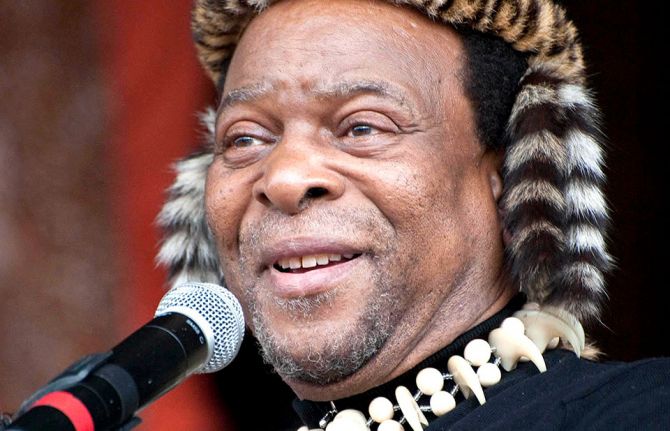
UNAIDS is deeply saddened by the death of His Majesty King Goodwill Zwelithini of the Zulu nation
17 March 2021 17 March 2021GENEVA, 17 March 2021—UNAIDS is saddened by the news that His Majesty King Goodwill Zwelithini has died and conveys its sincerest condolences to the Zulu royal family and to the wider Zulu nation.
“King Zwelithini was a change agent in South Africa’s AIDS response and encouraged his people to become actively engaged in reducing the impact of HIV in KwaZulu-Natal,” said UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima. “The King will be sorely missed both as a visionary leader and as a powerful and tireless advocate for people living with and affected by HIV.”
In 2009, King Zwelithini revived the practice of voluntary medical male circumcision (VMMC) among young Zulu men to help reduce the transmission of HIV. As a result of his leadership, KwaZulu-Natal, which has the highest prevalence of HIV in South Africa, has become a flagship for the effectiveness of VMMC as part of a combination of HIV prevention tools. The King was also a renowned advocate for people living with and affected by tuberculosis and stressed the need for community engagement to tackle difficult health issues, including HIV and tuberculosis.
In 2012, King Zwelithini spoke of the need for honesty between parents and their children in confronting the issues surrounding HIV prevention. “It is not easy, but we should speak the truth, because the love of truth is the spirit of men.”
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


Press Statement
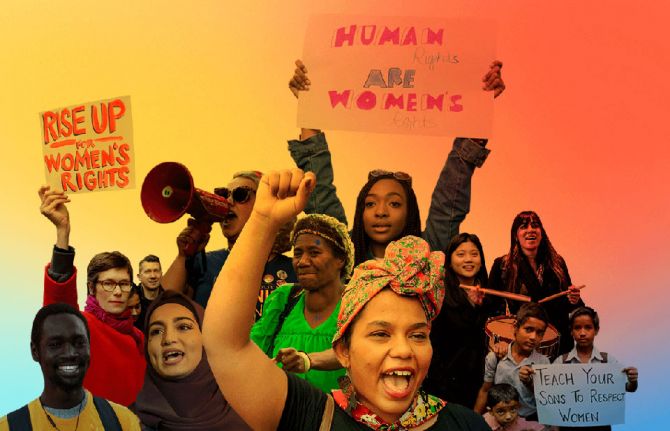
UNAIDS Executive Director's message on International Women’s Day 2021
08 March 2021 08 March 20218 March 2021
Winnie Byanyima
Executive Director of UNAIDS
Under-Secretary-General of the United Nations
Women leaders have provided a guiding light for the world in responding to the COVID-19 crisis, from heads of government to coordinators of grass-roots social movements. They have reminded the world how crucial it is to have critical numbers of women, in all their diversity, in positions of leadership.
But the COVID-19 crisis has seen progress towards equality pushed back. It has widened the gap between women and men in wealth, in income, in access to services, in the burden of unpaid care, in status and in power.
Up to 20 million more secondary school-aged girls could end up out of school following the crisis. Many may never go back to school or have access to skills and economic opportunities, and will be at greater risk of violence, poor health, poverty and more.
Two and a half million more girls are now at risk of child marriage in the next five years. There has been a dramatic increase in violence against women.
Pandemics such as COVID-19 and HIV magnify the fissures in society and exacerbate vulnerabilities. Gender-based and intersecting inequalities and violence hold back the lives of women and girls all over the world.
The pandemic has brought into sharp and painful focus that even before COVID-19 an estimated 34 million girls between the ages of 12 and 14 years were out of school, one in three women globally reported having experienced physical or sexual violence and women the world over worked longer hours for less or no pay.
Women who were already stigmatized are among those who are being hardest hit by the impacts of the pandemic. The sudden loss of the livelihoods of sex workers and their lack of access to health care and social protection have intensified their vulnerabilities, especially for those living with HIV. Many female migrants and precarious workers adversely affected by the pandemic are excluded from government relief and protection programmes, as well as health services. Stigma, discrimination and criminalization put transgender women, and women who use drugs, at heightened risk of HIV and other sexually transmitted infections, and hold them back from accessing HIV prevention, treatment and care services.
Recovery strategies cannot be gender-blind or gender-neutral: they must overturn the inequalities that hold women back.
Together, UNAIDS, UN Women, the United Nations Children’s Fund, the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization and the United Nations Population Fund have convened a broad movement, Education Plus, to work with governments to secure the transformative changes that will enable all of Africa’s adolescent girls to be in school, safe and strong. That includes all the girls who have been pushed out of school during the COVID-19 crisis and those who were excluded from school even before the crisis hit.
Overcoming the COVID-19 crisis, and ending new HIV infections and AIDS-related deaths, both require that we close in on the inequalities that drive vulnerabilities. The new global AIDS strategy 2021–2026 puts the rights and multiple and diverse needs of women and girls across their life cycle at the centre of the response: from preventing vertical transmission to providing access to quality education in safe and supportive environments to ensuring comprehensive sexuality education and holistic sexual and reproductive health services.
Gender inequality is not only wrong. It is dangerous. It weakens us all. A more equal world will be better able to respond to pandemics and other shocks; it will leave us healthier and safer and more prosperous.
Progress on gender equality has never been automatic. It has never been given, it has always been won.
We are inspired by the women’s movements leading the struggle for equality. The United Nations stands alongside you to advance a world where women and girls in all their diversity will thrive and take their rightful places as equals.
This International Women’s Day let’s support and celebrate women taking the lead.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)


Press Statement
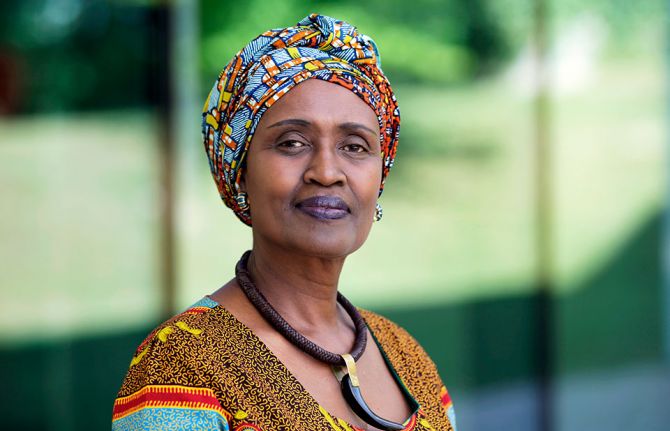
Message from the UNAIDS Executive Director on Zero Discrimination Day 2021
01 March 2021 01 March 2021This year’s Zero Discrimination Day is an especially poignant one.
It was said at first that viruses don’t discriminate. But as we’ve witnessed again, crises, and societies, do.
COVID-19 has magnified the fissures in society. It has seen marginalized communities, who were already on the edge, taking the hardest economic hit, getting stuck at the back of the line for vital services and getting scapegoated for the crisis.
Yet the crisis has also seen the most excluded communities being, once again, the first to step up to help—rooted in their expertise from experience, in their empathy and in their insistence that health for all and a recovery for all is possible.
UNAIDS joins with communities across the world in demanding equality. We say a resolute no to all inequalities—whether because of gender, income, race, disability, sexual orientation, ethnicity and religion. Such inequalities disfigure society and undermine justice and dignity.
We demand an end to discrimination, stigmatization and criminalization.
We challenge all institutions and all people of influence to not only be non-discriminatory, but to be anti-discrimination.
Discrimination kills. It exacerbates emergencies and it perpetuates pandemics.
The world is off track to end AIDS by 2030 not because of a lack of knowledge, capability or means but because of structural inequalities that stand in the way. For example, research shows that punitive laws regarding sexual orientation double the likelihood of acquiring HIV for gay men and other men who have sex with men. Repealing such laws is central to beating the HIV pandemic.
So too, discrimination against migrants and other excluded and stigmatized populations is obstructing their access to COVID-19 testing, treatment and support. This hurts everybody.
We are seeing the discrimination that scars our countries play out also at the international level. As new vaccines against COVID-19 have become available, there has been gross inequity. Just 10 countries have administered more than 75% of all COVID-19 vaccines, while more than 130 countries have not received a single dose. South Africa has called this vaccine apartheid. As the United Nations Secretary-General has said, “Vaccine equity is ultimately about human rights ... Vaccine nationalism denies it.” Around the world, and in every country, we must value every person as equally precious.
Ending inequalities will advance the human rights of all, make societies better prepared to beat COVID-19 and future pandemics and support economic recovery and stability.
We need to ensure everyone’s right to health through publicly provided and financed health care—and provide it respectfully to all, without reservation or judgement.
All of us need to call out discrimination wherever we see it, and to work to set an example.
A healthier, safer, more equal and prosperous world depends on it.
I am inspired by the leadership shown by communities facing discrimination. Their determination, courage and vision is our guiding light. The United Nations stands alongside, as a resolute ally for equality.
End inequalities. Demand zero discrimination.
Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Press centre
Download the printable version (PDF)


Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes the United Nations General Assembly decision to hold a high-level meeting on HIV and AIDS in 2021
25 February 2021 25 February 2021GENEVA, 25 February 2021—UNAIDS welcomes the United Nations General Assembly decision for a high-level meeting on HIV and AIDS to take place from 8 to 10 June 2021. The high-level meeting will review the progress made in reducing the impact of HIV since the last United Nations General Assembly high-level meeting on HIV and AIDS in 2016 and the General Assembly expects to adopt a new political declaration to guide the future direction of the response. The high-level meeting will take place as the world marks 40 years since the first case of AIDS was reported and 25 years of UNAIDS.
“World leaders must seize the opportunity offered by this new United Nations General Assembly high-level meeting on HIV and AIDS to maintain their focus and commitment on ending AIDS as a public health threat as part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development,” said Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director. “The AIDS epidemic is unfinished business and must be ended for everyone everywhere, including for young women and adolescent girls and for other groups of people disproportionately affected by HIV. The right to health belongs to all of us.”
Progress towards ending the AIDS epidemic as a public health threat by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals has been highly uneven and the global goals for 2020 adopted in the 2016 United Nations Political Declaration on Ending AIDS were not met. Stigma and discrimination, the marginalization and criminalization of entire communities and a lack of access to health, education and other essential services continue to fuel the epidemic. Women and girls in sub-Saharan Africa and key populations (gay men and other men who have sex with men, sex workers, transgender people, people who inject drugs and people in prison) and their partners globally continue to be disproportionately affected by the HIV epidemic.
UNAIDS is currently developing a new global AIDS strategy for 2021–2026 through a process that is inclusive of all stakeholders in the AIDS response. The final draft strategy will be considered for adoption by the UNAIDS Programme Coordinating Board in March 2021. The new global AIDS strategy will include new targets to ensure that no one is left behind in ending AIDS, wherever they live and whoever they are. By achieving these targets, the number of people newly infected with HIV would fall to 370 000 by 2025, and the number of people dying from AIDS-related illnesses would be reduced to 250 000 in 2025.
Even the gains already made against HIV are threatened by the disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. The high-level meeting creates an opportunity to ensure that the world bolsters the resiliency of the HIV response to date, commits to rapid recovery post-COVID-19 and applies the lessons learned from the colliding epidemics of HIV and COVID-19 to create more resilient societies and health systems that are ready to meet future health challenges.
“The AIDS response has taught us that global solidarity is critical to making sustained progress against the impact of health threats like COVID-19,” said Ms Byanyima. “There must be concerted international efforts to reduce inequalities between countries and within them to strengthen the world’s capacity to absorb and defeat future global health challenges that put lives and livelihoods at risk everywhere.”
UNAIDS expresses its appreciation for the hard work of the high-level meeting co-facilitators, the permanent missions to the United Nations of Australia and Namibia, in the adoption of the resolution as well as to the President of the General Assembly for leading the process.
Given the constraints imposed by measures taken to contain the COVID-19 pandemic, it has not yet been decided if the high-level meeting will be in-person, virtual or a hybrid of the two. In line with the resolution, UNAIDS encourages the highest level of participation of United Nations Member States and the inclusion of civil society organizations and people living with or at risk of HIV in delegations to the high-level meeting. UNAIDS also looks forward to the multistakeholder hearing as a key opportunity to hear the voices of people living with, at risk of and affected by HIV, including key populations.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


Press Statement
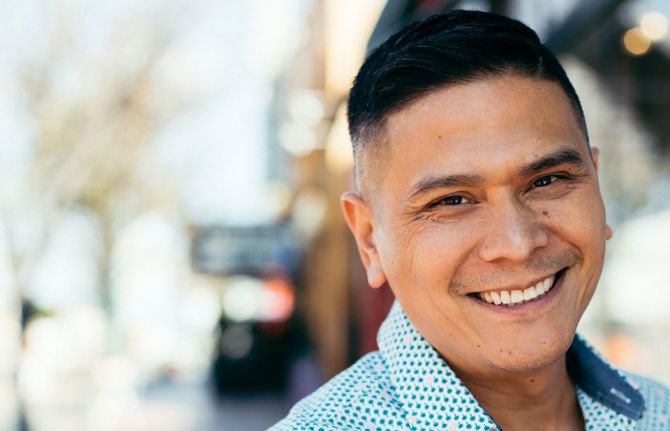
UNAIDS welcomes the appointment of Andrew Spieldenner as Executive Director of MPact
23 February 2021 23 February 2021GENEVA, 23 February 2021—UNAIDS warmly welcomes the appointment of Andrew Spieldenner as the Executive Director of MPact Global Action for Gay Men’s Health and Rights. MPact has been working since 2006 at the intersection of sexual health and human rights for gay and bisexual men and is linked to more than 120 community-based organizations in 62 countries. MPact has long been a key partner of UNAIDS—its work is critical for the promotion of the health and rights of gay and bisexual men and their communities and to ending AIDS.
“Andrew Spieldenner is a long-time respected HIV activist and scholar. In recent years, he has provided invaluable service to UNAIDS and the global AIDS response through his role as a delegate to the UNAIDS Programme Coordinating Board,” said Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director. “We look forward to continue working closely with him in this new position and to strengthen our relationship with MPact to address the challenges and inequalities faced by lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex communities in accessing health and fully enjoying their human rights around the globe.”
Mr Spieldenner’s commitment to people living with HIV, lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and intersex communities, feminist principles and racial justice has been evident throughout his 30 years of activism. A skilled organizer, communicator and mentor, he brings to his new position at MPact a long history of engagement with networks of people living with HIV. Working within local organizations, national networks of people living with HIV, health departments and academia, he has been at the centre of movements for social justice, leading from within, in partnership with the communities of which he is a part.
Mr Spieldenner will take up his new role on 1 March 2021.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.


Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes the United States of America’s decision to support women’s health, safety and rights
03 February 2021 03 February 2021GENEVA, 3 February 2021—UNAIDS warmly welcomes the announcement by the President of the United States of America, Joe Biden, that he has rescinded the Protecting Life in Global Health Assistance Policy (PLGHA, previously known as the Mexico City Policy). The policy required foreign nongovernmental organizations to certify that they would not perform or actively promote abortion using funds from any source (including non-United States funds) as a condition of receiving United States Government funding.
“Rescinding the PLGHA is a strong demonstration of the new United States Administration’s commitment to supporting women to claim their rights and to access sexual and reproductive health and rights information and services,” said Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director. “We look forward to working closely with the new United States Administration to ensure that all women and girls can exercise their human rights and get the sexual and reproductive health information and services they want and need.”
The former United States Administration took previous restrictions established by the Mexico City Policy to a new level by applying the policy to global health assistance provided by all executive departments and agencies. This severely limited access to critical sexual and reproductive health-care services and stifled local advocacy efforts, in turn undermining human rights in general and sexual and reproductive health and rights in particular worldwide.
UNAIDS welcomes the White House’s call to waive conditions related to the PLGHA in any current grants with immediate effect, to notify current grantees, as soon as possible, that these conditions have been waived and to cease imposing these conditions in any future assistance awards.
“Women and girls having full access to their sexual and reproductive health and rights is closely connected to their overall safety, health and well-being. We hope that this will inform the passage of the Global Health, Empowerment and Rights Act—legislation designed to permanently repeal the PLGHA,” added Ms Byanyima.
UNAIDS also warmly welcomes the announcement by the President that the United States will restore funding to the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), a key UNAIDS cosponsoring organization working around the world to provide reproductive health care for women and young people. UNAIDS appreciates the commitment by the United States Secretary of State, Anthony Blinken, to appropriate US$ 32.5 million in support for UNFPA this year.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Region/country


Press Statement
UNAIDS calls for the release of five humanitarian workers detained in the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela
29 January 2021 29 January 2021GENEVA, 29 January 2021—UNAIDS is deeply troubled and concerned about the detention by military police of the Venezuelan citizens and humanitarian workers Johán León Reyes, Yordy Bermúdez, Layners Gutiérrez Díaz, Alejandro Gómez Di Maggio and Luis Ferrebuz, who are members of the nongovernmental organization Azul Positivo. The five have been held since 12 January 2021.
“I call on the Venezuelan authorities to release from police custody the five humanitarians working for the nongovernmental organization Azul Positivo, and to return essential equipment seized at the time of their arrest,” said Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director. “A strong and empowered civil society plays a central role in providing much-needed services to the most vulnerable people and is critical to making progress against the HIV pandemic and other health threats in the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela.”
Azul Positivo was established in 2004 to work on the prevention of HIV in the state of Zulia, Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela. UNAIDS has supported Azul Positivo’s work for many years and has witnessed the positive impact of their contributions to the community.
UNAIDS is strongly supportive of the full empowerment and engagement of civil society organizations in the AIDS response and in humanitarian work. It looks forward to continuing its partnership with community and civil society organizations in the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, as well as with government officials, in ensuring that all people affected by HIV have access to HIV prevention, treatment and social support services and that their human rights are protected.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Our work
Region/country


Press Statement
UNAIDS calls for the LGBT community in Uganda to be treated with respect and dignity at all times
12 January 2021 12 January 2021GENEVA, 12 January 2021—UNAIDS is concerned that the vilification of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) communities in Uganda could lead to heightened violence, stigma and discrimination against them and reduce their access to HIV and other essential services. In a recent media interview, the President, Yoweri Museveni, described being LGBT as a “deviation”.
“Using offensive language that describes LGBT people as “deviant” is simply wrong,” said Winnie Byanyima, Executive Director of UNAIDS. “Stigma and discrimination based on sexual orientation violates rights and keeps people away from HIV testing, treatment, prevention and care services. The HIV epidemic can never end while some groups of people are excluded from health services.”
UNAIDS advocates with legislators, other government authorities and civil society globally to establish anti-discrimination and protective laws to eliminate the discrimination and violence faced by LGBT people and to advance the right to health for all people without exception.
Uganda has made considerable progress against the HIV epidemic in recent years. Of the estimated 1.5 million people living with HIV in Uganda in 2019, around 1.3 million were aware of their HIV status and 1.2 million were on treatment. More than 95% of pregnant and breastfeeding women living with HIV in Uganda receive antiretroviral therapy to keep them healthy and prevent transmission of the virus to their children.
However, in Uganda gay men and other men who have sex with men are less likely to have access to the HIV testing, treatment, prevention and care services that could keep them healthy and well, in part because of the stigma and discrimination they face in health-care settings and throughout society.
“It’s clear that to end the AIDS epidemic in Uganda there is a need to build a more inclusive society where everyone enjoys the right to health. UNAIDS stands ready to work with all partners to end stigma and discrimination against the LGBT community and achieve the full respect of their universal human rights,” said Ms Byanyima.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
Our work
Region/country

Press Statement
UNAIDS welcomes investments from Sweden and Germany for the responses to HIV and COVID-19
18 December 2020 18 December 2020GENEVA, 18 December 2020— UNAIDS strongly welcomes the announcement by Sweden at the 47th meeting of UNAIDS Programme Coordinating Board to renew its annual funding commitment to UNAIDS of SEK300 million in core funding for 2021, equivalent to 36 million USD, demonstrating the country’s continued leadership in the global AIDS response. In making the announcement, Sweden underscored UNAIDS role in working for sexual and reproductive health and rights.
UNAIDS also welcomes Germany’s announcement, at the same meeting, of its decision to invest an additional €5 million in UNAIDS complementary responses to the HIV and COVID-19 epidemics next year. This builds on the country’s contribution of €20 million to UNAIDS’ HIV and COVID-19 response in June this year and is on top of Germany`s annual contribution to UNAIDS of €5 million. In making the announcement, Germany recognized UNAIDS’ outstanding work in responding to the colliding epidemics of HIV and COVID-19 and called on other donors to consider increasing their contributions.
“I want to thank Sweden and Germany for their strong leadership in the AIDS response as well as their confidence in and support for UNAIDS,” said UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima. “These contributions will allow UNAIDS to maintain our response to the HIV epidemic, while mitigating the effects of COVID-19 on vulnerable groups of people and mobilizing the AIDS response, its infrastructure and expertise against COVID-19.”


Press Statement
UNAIDS applauds the vote by Bhutan’s parliament to repeal laws that criminalize and discriminate against LGBT people
14 December 2020 14 December 2020GENEVA, 14 December 2020—UNAIDS congratulates Bhutan’s parliament on voting to repeal Sections 213 and 214 of the country’s Penal Code. Those provisions criminalized certain private sexual acts and led to discrimination against and the marginalization of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people. The country’s parliament voted for the repeal on Human Rights Day, 10 December.
“I commend Bhutan’s parliamentarians for voting to create a more compassionate, tolerant and inclusive society and for recognizing that the country’s LGBT people deserve privacy, respect and dignity,” said Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director. “This step taken on Human Rights Day will also help to ensure that LGBT people in Bhutan receive the essential services they need, including HIV treatment, prevention and care services.”
Bhutan becomes the latest country to decriminalize consensual same-sex sexual relations. Since 2014, Angola, Botswana, Gabon, India, Mozambique, Nauru, Palau, the Seychelles and Trinidad and Tobago have all taken the same measure. However, consensual same-sex sexual relations remain criminalized in at least 68 countries and territories worldwide.
Criminalization of consensual same-sex sexual relations prevents people from accessing and using HIV prevention, testing and treatment services and increases their risk of acquiring HIV. It legitimizes stigma, discrimination and violence against LGBT people and is a human rights violation.
Globally, the risk of acquiring HIV is 26 times higher among gay men and other men who have sex with men than among the general population and 13 times higher for transgender people. Prohibitive legal and policy environments and a lack of tailored services for key populations increase their vulnerability to HIV. UNAIDS urges countries to ensure the full respect of the human rights of all people, regardless of their sexual orientation, through repealing laws that prohibit sex between consenting adults in private, enforcing laws to protect people from violence and discrimination, addressing homophobia and transphobia and ensuring that crucial health services are made available.
UNAIDS
The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) leads and inspires the world to achieve its shared vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths. UNAIDS unites the efforts of 11 UN organizations—UNHCR, UNICEF, WFP, UNDP, UNFPA, UNODC, UN Women, ILO, UNESCO, WHO and the World Bank—and works closely with global and national partners towards ending the AIDS epidemic by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. Learn more at unaids.org and connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and YouTube.
