Feature Story
New long-acting HIV prevention options for women and girls in an era of choice
14 October 2024
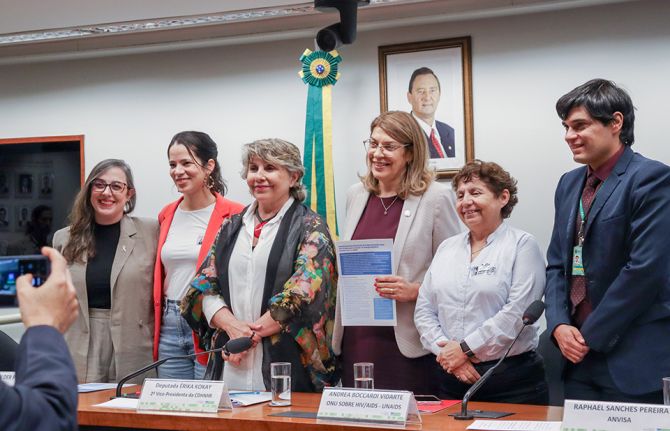
14 October 2024 14 October 2024New long-acting technologies are changing the HIV prevention landscape. In recent years, innovation in pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) has accelerated. Long acting injectable cabotegravir and the dapivirine vaginal ring as innovative formulations of PrEP have already joined oral PrEP containing tenofovir as WHO-recommended effective and acceptable options for HIV prevention, and there are additional antiretroviral-based options on the immediate horizon. These options complement other effective, non-antiretroviral-based HIV prevention products including condoms and lubricants, and harm reduction strategies.
This year clinical trial results for PURPOSE 1 and 2 showed the high prevention effectiveness of the 6-monthly long-acting injectable drug, lenacapavir for cisgender adolescent girls and women, cisgender men and transgender women. Among the cisgender adolescent girls and women participating in the trial, no HIV acquisitions were recorded during 12 months of follow-up among the women who received injectable lenacapavir. The Global HIV Prevention Coalition (GPC), UNAIDS and other partners called on Gilead Sciences to accelerate their efforts in ensuring that it is made available, accessible and cost effective especially to low- and middle-income countries. This twice-yearly injection is a promising option and offers increased choice, discretion and convenience for people who may benefit from HIV prevention.
In October 2024, at the Research for Prevention (R4P) conference in Peru, the Population Council announced phase 1 trial results from IPM 054, showing that the three-month dapivirine ring is as safe as the currently available one-month ring with similar levels of drug release. The 3-month ring like the 1-month ring is a woman-controlled option but would be more cost effective (an estimated 60% reduction in cost per user) and potentially an even more convenient HIV prevention option for women and adolescent girls.
“We need to follow the science, and the science has shown us that by making a range of effective HIV prevention options available and accessible, we can stop HIV transmission and drop new infections by addressing biomedical, behavioral and structural drivers simultaneously. Ending AIDS remains a political and financial choice”, says Angeli Achrekar, UNAIDS Deputy Executive Director Programmes.
This complements a partnership announcement by the Global Fund and the Children’s Investment Fund Foundation (CIFF) of an USD 2 million initiative for 2024-2025 to purchase an estimated 150 000 dapivirine vaginal rings for use as PrEP in the Global Fund grant implementing countries. This would increase accessibility to one of the most discreet HIV prevention options for women and adolescent girls.
The World Health Organization (WHO) PrEP Implementation Tool Provider Module for Oral and Long Acting PrEP, launched in July 2024, integrates clinical service delivery guidance for the three WHO recommended PrEP products (oral PrEP, the dapivirine vaginal ring and long-acting injectable cabotegravir) by a range of different providers in clinical or community settings and emphasizes the importance of access and choice.
These strategic advancements align to the HIV Prevention Choice Manifesto For Women and Girls in Africa that calls for prevention options to be made choices and urges that research and development of new HIV prevention options actual choices, thereby empowering women and girls to take control of their health and bodies. It also emphasizes the importance of ongoing research and development of innovative HIV prevention methods.
“Adolescent girls and women are gaining access to an increasing range of safe and effective options. Scale-up of HIV prevention will depend on supporting access to choice, strong country leadership and an enabling environment. An HIV free future for girls is possible, but only if the global community comes together with ambitious plans to make this range of PrEP options available with speed, scale and equity,” says Mitchell Warren, Executive Director, AVAC and GPC, Co-chair.
The GPC co-convened, by UNAIDS and UNFPA, will continue to work with its partners to accelerate HIV prevention to achieve the global target of less than 370 000 new HIV infections annually by 2025.
About the GPC
In 2017, a global coalition of United Nations Member States, donors, civil society organizations, and implementers was established to support global efforts to accelerate HIV prevention. Membership includes 38 of the highest HIV-burden countries, UNAIDS Cosponsors, donors, civil society, and private sector organizations. The overarching goal of the Global HIV Prevention Coalition is to strengthen and sustain a political commitment to primary prevention by setting a common agenda among key policymakers, funders, and program implementers.
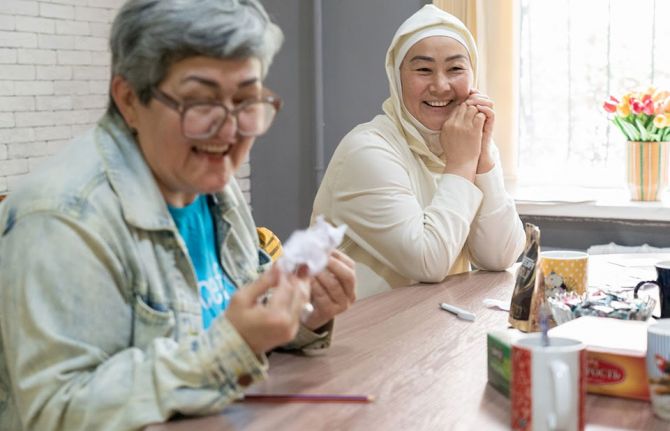


Feature Story
The power of women supporting women - Mentor program for women living with and affected by HIV in Kazakhstan
13 September 2024
13 September 2024 13 September 2024The Mentor programme for women in Kazakhstan was established to empower women living with or affected by HIV by connecting them with mentors who share their life experiences and provide critical support during challenging times. Co-financed by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Kazakhstan and supported by UNAIDS, the program creates a safe space for women to learn, grow, and draw strength from one another. Through training seminars, support groups, and one-on-one mentoring, it helps women overcome stigma, rebuild their lives, and find their purpose.
Meet three inspiring leaders from this programme—women who never saw themselves as heroes but are, indeed, changing lives.
Halima
Several years ago, Halima found herself at a crisis center for women victims of domestic violence in Almaty, Kazakhstan. She was at rock bottom—diagnosed with HIV, grieving the loss of her second son, and trapped in an abusive marriage with a husband who drank heavily and often turned violent. Raised in a family that valued tradition, Halima felt compelled to keep the peace at all costs, but the weight of her daily life became unbearable.
At her lowest point, an elderly doctor’s advice pushed her into action: “If you want your eldest son to end up in an orphanage, your husband homeless, and you in a mental hospital, you are sadly following that path.” Determined to change her fate, Halima sought help at the crisis center, which she credits with helping her climb out of the “dark hole” of depression.
Today, Halima is helping other women in the mentoring programme. She shares her story with women, believing that her experiences can inspire others to seek life-saving HIV treatment and persevere.
"I make sure to give each person my undivided attention so I can explain in simple terms what HIV is, what an undetectable viral load means, and how to get better,” she says.
Her work extends beyond Almaty, reaching women in rural areas where information about HIV and access to services is limited. “I have no special education, but I love learning. While I’m cleaning or mopping the floors, I listen to psychologists and doctors on my headphones,” she says, knowing that every bit of knowledge helps her make a difference.
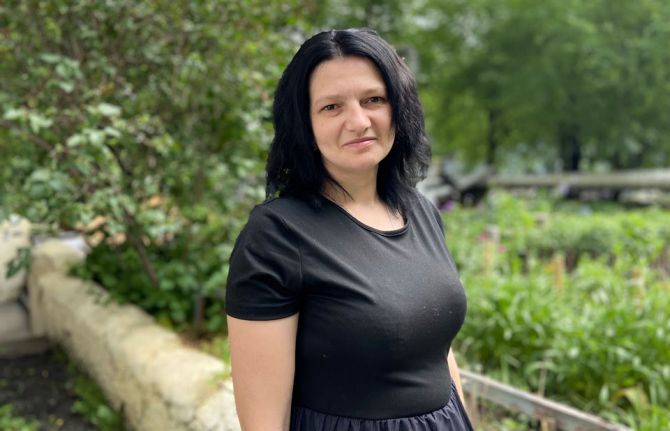
Lena
“This is a complex group,” says Lena from Pavlodar, Kazakhstan. She works with 17 women in a mentoring programme. Many of the women use drugs, have experienced domestic violence or have been in prison. Lena, aged 55, used drugs for over 20 years, but she has been drug-free for seven years, crediting opioid agonist maintenance therapy for helping her quit.
“I went through all this myself. I remember how it was using drugs: I fell asleep—it’s winter. Woke up—summer,” she says. “If a person comes to therapy out of desperation, does not want to steal or torment their parents and loved ones, this programme can help them.”
The therapy helps mitigate the need for drugs, but Lena emphasizes “it is important that peers and psychologists work with people and prepare them to leave the programme and have access to essential HIV prevention services and treatment”.
After being released from prison nearly a year ago, Lena became a peer consultant in the women’s mentoring programme.
“The problem for many people who use drugs is that they live with HIV and TB but cannot access available services or receive therapy,” Lena explains. Without a home or family, they are invisible to the social protection system and are often driven into desperate situations. “They need a helping hand. They are humans and live next to us."
Lena helps some people register for medical or social support facilities, and others to get treatment. She plans to meet with the akim (mayor) to propose a project to create a support system for people who are left behind. Lena believes there should be no situations where a person is alone and cannot be admitted to a home for disabled or elderly people because they are living with HIV. It is crucial to revise the laws so that everyone is allowed access to social institutions.
Lena is dedicated to the programme. “I am reborn from this work. My eyes light up, and I feel strong and ready to help,” she says.
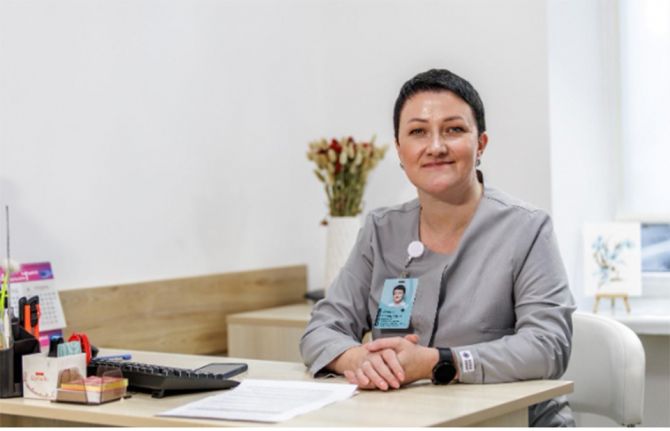
Zulfiya
Zulfiya, a mother of three who has lived with HIV for nearly 20 years, uses her experience to support adolescents and young women in the program. “My task is to help them accept their diagnosis, start treatment, and stick to their medication,” she explains. She refers women to psychologists, social workers, or lawyers when additional support is needed. Zulfiya understands the denial many women face; she felt it herself two decades ago. Inspired by her son, an activist in the Teenager youth organization for adolescents living with HIV, she found her calling in guiding women who never thought HIV would touch their lives.
Connecting women with other women in a predominantly male-dominated society is the foundation of the mentoring program. “Women in Kazakhstan are often forced to solve a wide range of problems themselves, whether it’s financial difficulties, lack of help, or protection from violence,” says Elena Rastokina, coordinator of the Mentor Programme for Women. “They are not used to uniting in women’s communities, do not know how to ask for help, and often do not know their rights.” Despite the challenges, she is immensely proud of what the mentors have achieved. “When women support each other, they find strength they never knew they had. We need each other, and together, we can change lives.”
The mentoring programme covers 10 regions of the country. Dozens of women have received help. Some have learnt a new skill and found a job, and others have managed to accept their diagnosis and restore family ties. With help from the programme, many women who use drugs have managed to quit active drug use, improve adherence to life-saving HIV and TB treatment, and reconnect with the community.
For Aliya Bokazhanova, UNAIDS Country Director a.i. in Kazakhstan, these are incremental steps to empowering women from key populations. “Women living with HIV have the opportunity to develop and receive the necessary support and inspiration from experienced mentors, which contributes to their self-realization and integration into society,” she says.
As of 2024, there are an estimated 40 000 [35 000–46 000] people living with HIV in Kazakhstan. New HIV infections are mostly among people from key populations (people who use drugs, gay men and other men who have sex with men, sex workers, and people in prisons and other closed settings). HIV prevalence among people who inject drugs is almost 7%, compared with 0.3% in the general population.
Region/country
Related




Feature Story
Interactive health and HIV game app reaches more than 300 000 young people in Côte d’Ivoire
09 September 2024
09 September 2024 09 September 2024Four weeks before the African Cup of Nations football tournament kicked off it was down to the wire. José Fardon, a Côte d’Ivoire web designer and digital developer, had his whole team frantically working on a special edition of an interactive health and HIV game app, called "A l'Assaut du Sida", ‘Tackling AIDS’ (AADS) to coincide with the tournament.
The UNAIDS team had secured funds for the latest rendition of the online game and had rallied UNICEF and the Global Fund to chip in.
“We had launched various versions of the game in the past, but this required a different look and feel to gel with the sporting event,” said Mr Fardon, founder of SYL.
They also needed a final approval from the National AIDS Programme (PNLS).
"Out of the many initiatives put forward ahead of the CAN, the online app really appealed to us because we knew it would not only reach the target audience, it would also make an impact,” said Eboi Ehui, PNLS Coordinating Director. “This is a generation that has never seen the ravages of AIDS so they have felt like it isn’t a problem but it is.”
The success was beyond anyone’s expectations.
The 20,000 tournament volunteers recruited by the Ministry of Youth not only played the online game themselves but they fanned out around the stadiums promoting the game by sharing the QR code with the hundreds of thousands of supporters. And with various prize giveaways during the tournament and afterwards, more and more people downloaded the app to play. Since mid-January 2024, AADS has reached nearly 200,000 adolescents and young people with the latest version reaching a lot of young boys and men (cumulatively, the three versions have reached almost 300 000 people.)
“When I think back, this idea germinated in 2016 as a tool for schools then was launched at the Francophonie Games a year later but now, we really brought it to the general public,” Mr Fardon said. “I am so proud we never gave up.”
His determination impressed more than one person.
In eight years, he convinced UNAIDS staff, the country’s Ministry of Health in close collaboration with PNLS, the Ministry of Education, the Ministry of Youth and countless partners on the ground.
UNAIDS Country Director Henk Van Renterghem, like his predecessors before him, saw the value and potential of using digital technology to reach adolescents and young people. “General knowledge about HIV and overall comprehensive sexual education has decreased and young people are struggling with so many choices that this easy to download game is without a doubt relevant,” he said.
In July 2023, he explained, the National AIDS Council was alerted by the results of a survey and beseeched HIV partners to step up communication and education efforts.
“Despite the fact that young people have more access to information through the internet and social media than ever before, many young people are struggling to make informed decisions about their sexual relations,” said Mr Van Renterghem. For example, the survey revealed that only 40% knew that medicine (anti-retroviral treatment) existed for HIV and 39% of girls (29% of boys) did not know that condoms prevented HIV transmission. Last year, 20% of new HIV infections in the country were among 15–24-year-olds, according to government data.
As a result, UNAIDS staff along with SYL, vetted and increased the number of questions expanding prevention info.
He and his staff were particularly happy because they also succeeded in expanding the scope of the content.
In went the fact that people with HIV on effective treatment can achieve an undetectable viral load and cannot transmit the virus (U=U) plus stuff about stigma & discrimination, human rights, gender equality and gender-based violence – all structural drivers of HIV.
The full game of 400 questions is like a quiz with additional information popping up. Players score points by advancing through 40 sets of ten questions. At least seven correct answers are needed to advance to the next level. It can take up to an hour to get to the last round and when the updated pilot was tested in October and November of 2023, young people responded well.
Two of the young players who scored in the best percentile agreed.
“The game really taught me a lot. There are a lot of facts about HIV and sexually transmitted diseases,” said Marie Koffi. For Wilfried Touré he said, “I learned a lot of things that I had no idea about from tuberculosis to HIV and even on a personal level I picked things up.”
Going forward national partners now want to distribute a scholastic version of the game to all Côte d’Ivoire schools.
During the final awards ceremony at the end of March, Côte d’Ivoire’s Minister of Health, Pierre Dimba, was clear. “This fun and educational online game is a response to young people's need for true and accurate information via social media,” he said. “The popularity of this game among teenagers is a real testimony that adapting our communication strategies to the habits and needs of young people pays off.”
In Mr Van Renterghem’s mind, Côte d’Ivoire should be proud.
“This home-grown low-cost tool will help us sustain our HIV prevention efforts as international funding will inevitably dwindle.”
That is in part why Mr Fardon and UN partners are dreaming even bigger.
“We would like to launch the app-based game in neighboring countries and eventually roll this out throughout western and central Africa,” he said.
“The sky is the limit.”
More information
Demographic and Health Survey
Region/country
Related
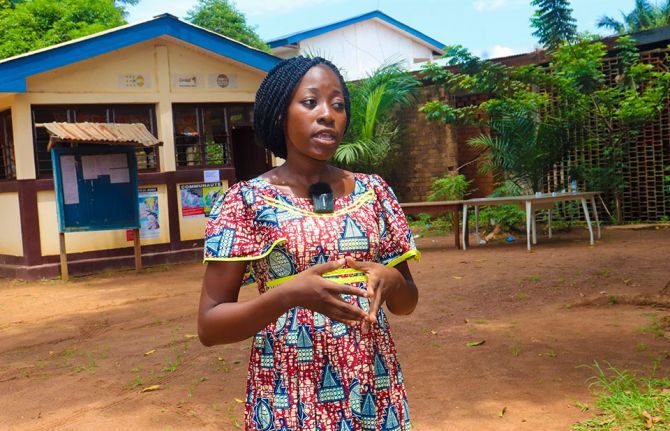




Feature Story
Bridging gaps: sex education saves lives in Central African Republic
03 September 2024
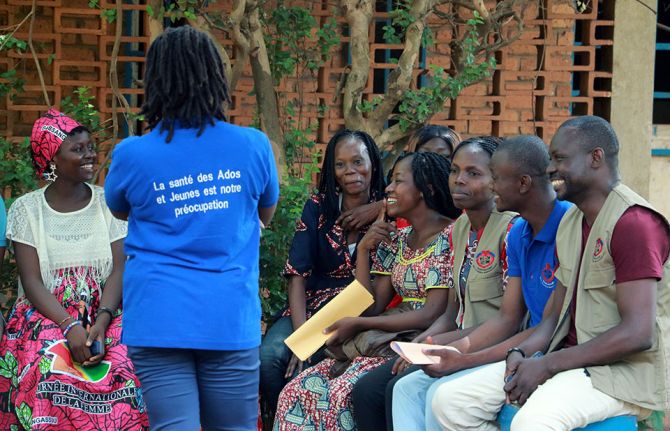
03 September 2024 03 September 2024In a modest neighborhood of Bangui, Central African Republic’s capital city, Gniwali Ndangou is rushing to work. She’s a peer educator and community health worker at a youth sexual education centre, CISJEU.
The same centre that saved her life.
I'm an orphan," she said, “I am the youngest of three sisters.” Throughout her childhood, her legal guardian told her to take pills saying it was anti-malaria and headache medicine. “I was the only one who took treatment every day and it never stopped.”
After threatening to stop taking pills when she was 17 years old, her sister finally told her the truth. She was born with HIV.
Gniwali couldn’t believe the litany of lies. Having recently been forced to quit school as her adopted family struggled to make ends meet, she once again felt abandoned.
“Many times, I tried to commit suicide… I wanted to end my life,” she said.
Her sister Astrid said she tried to pull her youngest sibling out of despair and kept hammering to her: “There are no differences between us, we are all humans.”
At her sister’s urging, Gniwali sought help at a youth center, Centre d’information et d’éducation sexuelle des jeunes (Center for Youth Sexual Education and Information) known as CISJEU. Established in 1994, CISJEU has been a beacon of hope for many young people like Gniwali. They offer community-led services ranging from HIV prevention to HIV testing to peer-supported treatment initiation and adherence.
War and extreme poverty have greatly increased premature death in Central African Republic, leaving seventy-eight percent of the population under 35 years old. Young people struggle to receive an education with less than 4 in 10 adults literate. Gender inequality and gender-based violence also make young girls particularly vulnerable to HIV infection. Out of the 10,000 yearly new HIV infections, 3000 are among 15-24 years old with more than two female infections for every one male infection.
According to a UNICEF survey, less than 20% of young people possess comprehensive knowledge about HIV prevention. The youth center uses peer educators to bridge this knowledge gap and provide youth-friendly services. "We've trained and deployed 160 peer educators (80 in schools while the others are at youth centers) across different districts of Bangui and beyond, ensuring effective outreach and health and body awareness," said Michael Guéret, a program officer at CISJEU.
Chris Fontaine, former UNAIDS Country Director, underscores the importance of peer-led initiatives, “Addressing HIV and sexual health among young people in CAR is not just a health issue but a critical component of sustainable development and peace consolidation.”
With support from UNAIDS and the Ministry of Health, CISJEU has attained the right to distribute HIV medicine, antiretroviral therapy, among the community.
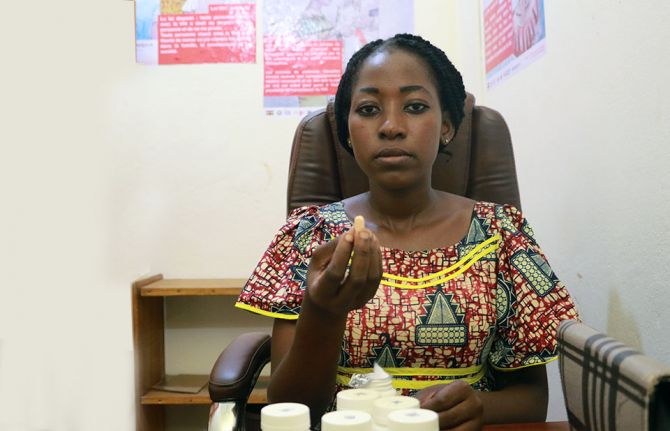
For Gniwali, CISJEU became more than a sanctuary. Through training programs, she evolved from a beneficiary to a peer educator and community healthcare provider. “I received various certifications such as mobile HIV testing, and psychosocial support."
Leading discussion groups and dispensing life-saving antiretroviral medications to young people, she inspires young women to take care of their health. Her message is clear and powerful: "Being a young woman isn't easy. We must educate ourselves about this disease, fight against it, and prevent its spread in our country.”
Watch
Region/country
Related
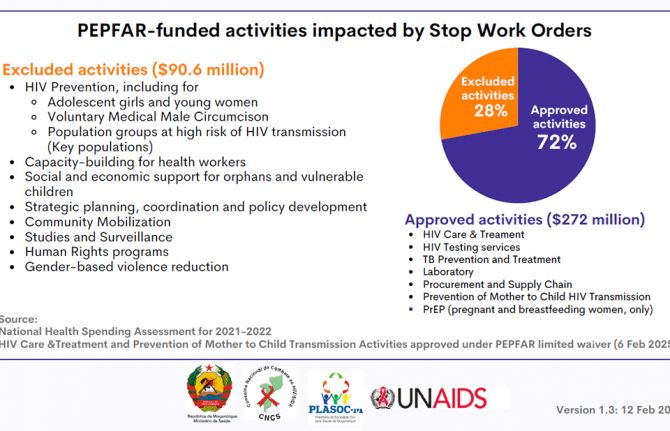
 Impact of the pause of US foreign assistance in Côte d'Ivoire
Impact of the pause of US foreign assistance in Côte d'Ivoire

19 February 2025




Feature Story
Working to end gender-based violence in fragile settings
28 August 2024
28 August 2024 28 August 2024Across the world, spikes in instability, displacement, and conflict are exacerbating people’s vulnerability to gender-based violence and to HIV.
“Gender-based violence is an egregious human rights violation. It is also a driver of the AIDS pandemic, especially in fragile states. Tackling gender-based violence is essential to uphold the right to health and life for everyone,” says UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima.
Efforts to prevent and to respond to HIV and gender-based violence in fragile settings remain partial, isolated, and unstable despite normative commitments made at the global level.
Fragility is described by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development as “…the combination of exposure to risk and insufficient coping capacities of the state, system, and/or communities to manage, absorb or mitigate those risks.”
The new report, The Missing Link: Rethinking and reprioritizing HIV and gender-based violence in fragile settings, reveals the results of a study on the linkages between HIV and gender-based violence in fragile settings. This issue is explored through the lens of peace support operations. Work was partially funded through the generous contribution of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg to UNAIDS.
The study examines the mandates and objectives of peace support operations, revealing that HIV and gender-based violence remain deprioritized, with responses of peace support operations often disconnected. Several challenges in translating agreed-upon principles into actionable results are identified and recommendations are offered to address these barriers.
“This report provides a crucial guide to support strategic decision-making in HIV and GBV advocacy in peace support operations and will be a vital tool for addressing these urgent challenges effectively,” says Sihaka Tsemo, Director, UNAIDS Liaison Office to the African Union & UNECA.
The report provides guidance to duty bearers across the development, peace and security and humanitarian arenas.
In the Democratic Republic of the Congo, for instance, the UN peacekeeping mission, MONUSCO, is in an active process of withdrawal and transition. UNAIDS Country Director, Susan Kasedde, reflects on the vital role of the UN’s Joint Programme on HIV and AIDS in addressing the multifaceted interlinkages between HIV and gender-based violence in fragile settings:
“The Joint Programme brings together invaluable expertise for a holistic response and plays a crucial role in strengthening state capacity to lead and deliver, through supporting strengthened systems for accountability and governance, and through facilitating broad partnerships, including with communities, to enable transformative and sustainable changes and take to scale effective models for integrated delivery of HIV interventions on the ground.”
In Mali, the decade-old Multidimensional Integrated Stabilization Mission has recently completed its withdrawal. UNAIDS Country Director, Marc Saba, explains the role of the United Nations Gender Thematic Group in supporting internally displaced persons in localities affected by insecurity and the humanitarian crisis.
“In the past 8 months the UN Country Team in Mali, under the leadership of UN Women, has provided capacity building, food support and funds to carry out income-generating activities to over 1000 women, young girls and men in vulnerable situations. In addition, the UN Joint Team on AIDS plans to launch a study on HIV and gender in humanitarian contexts, with the goal of collecting and analysing data to better understand these issues within the humanitarian response.”
The Missing Link report underscores the critical need for well-coordinated, multisectoral approaches to address HIV and gender-based violence effectively in fragile settings. It contributes to a wider conversation which requires further research, collaboration and multisectoral engagement. It provides recommendations for building a more holistic, human-rights based and gender transformative approach to addressing and eliminating gender-based violence in all its forms in fragile settings.
“To end gender-based violence and to end AIDS, depends on uniting efforts across multiple sectors, on survivor and community-centred approaches, and on sustained investment.” says Winnie Byanyima, UNAIDS Executive Director.
The issues raised in the report will be discussed in a stakeholder roundtable scheduled for 10 September 2024.
The webinar will be via Zoom on 10 September 2024 at 13:30-15:00, Geneva, Switzerland time. It will be 11:30 in Dakar, Senegal, and 14:30 in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Simultaneous interpretation into English and French will be provided.
Kindly click on the link below to register and participate, and do not hesitate to share information about the webinar with your networks.
Related


Feature Story
Developing the 2030 recommended HIV targets: framing the future of the HIV response
26 July 2024
26 July 2024 26 July 2024UNAIDS has launched the 2030 target-setting process that will provide the framework for the next Global AIDS Strategy. A Global Targets Task Team (GTT) composed of 33 experts from governments, civil society and communities, donors, multilateral organizations and academic public health experts will propose the targets building on the targets set for 2025. The Global Task Team is co-chaired by Chewe Luo, former Director HIV at UNICEF and Michel Kazatchkine, former Executive Director at the Global Fund.
The targets and strategy will underpin and inform the June 2026 High Level meeting on AIDS. The 2030 HIV targets will provide milestones within the SDG 2030 targets of reducing new HIV infections and AIDS-related deaths.
As highlighted in the July 2024 Global AIDS Update – the Urgency of Now : AIDS at a crossroads, there will be millions of people living with HIV in 2030 and beyond. The next set of targets will focus on the services and systems that countries need to have in place to ensure a sustainable country-owned response after 2030.
In defining the targets, the GTT will consider the balance of proposed thematic areas, measurability, evidence of impact of interventions, gender-sensitivity and human rights. These targets will only be successful if they are adopted by countries. Ensuring their relevance to countries and country engagement will be fundamental to this process.
The GTT has been undertaking an initial scoping phase and will work until November 2024 to develop a set of recommended targets to UNAIDS. These targets will become the foundations of the next Global AIDS Strategy consultation process.
Related




Feature Story
Women living with HIV continue to face violations of their sexual and reproductive rights—including coercion into sterilization
24 July 2024
24 July 2024 24 July 2024Women living with HIV including women from key populations continue to suffer widespread reproductive coercion, mistreatment, and neglect when seeking reproductive health services and rights around the world, a new report by the International Community of Women Living with HIV (ICW) has revealed today. The report was launched at a joint ICW/UNAIDS event at the 25th International AIDS Conference taking place in Munich, Germany.
The report, Confronting Coercion: A global scan of coercion, mistreatment and abuse experienced by women living with HIV in reproductive and sexual health services, shows that women living with HIV face practices that undermine their bodily autonomy. Reproductive choices are monitored, and women are subjected to various coercive practices.
The report documents experiences of sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) violations and violence faced by women living with HIV and women from key populations from more than 60 countries across 3 regions and offers concrete actions for the reduction of coercive practices.
“This report offers a chilling reality of what women living with HIV experience every day in their struggle to realize their full sexual and reproductive health rights,” said Charity T. Mkona, Global Coercion Scan Committee, ICW ISC Global Chairperson. "For women living with HIV who have been subjected to coercive practices, mistreatment or abuse, the ability to heal and realize their full sexual and reproductive health and rights, demands accountability and justice."
The report reveals that reproductive coercion and mistreatment of women and gender diverse people living with HIV in SRHR services are a common, persistent, and widespread issues that require urgent action. Women living with HIV who reported engagement in sex work, drug use, or had disabilities reported experiencing coercive practices at higher rates than other women living with HIV.
Younger women living with HIV and women living with HIV who were migrants were also more likely to have experienced coercive practices than older women and women who were not migrants. Women have reported experiencing a lack of confidentiality and consensual care, as well as inappropriate medical interventions, such as unnecessary caesarean sections and forced or coerced abortions. Denial of care, stigmatizing comments or insults, and various forms of abuse - verbal, emotional, physical and sexual - were also documented.
While information about sexual and reproductive health and rights of women may be supplied to them, it is not always accurate, comprehensive, or up-to-date to empower them to claim their rights and often does not reflect the realities of women's lives.
"To end coercive practices experienced by women living with HIV, we must recognize the systemic and entrenched nature of these violations and understands that reform requires a systemic sea change and culture shift that respects women's bodily autonomy.” Sophie Brion, Director of Global Programmes at ICW.
“In a world where significant scientific advancements have been made in the treatment of HIV—including breakthroughs that allow women living with HIV whose viral load is undetectable to give birth to HIV negative babies—it’s shocking that some health care workers are not informed that women living with HIV can give birth without transmitting the virus,” said Christine Stegling, UNAIDS Deputy Executive Director for Policy, Advocacy and Knowledge. “This lack of education and coercive practices, including the forced sterilization of women living with HIV, must stop immediately.”
ICW is calling on governments worldwide, including donors and ministries of health, to eliminate these harmful practices. The organization is also calling on governments to ensure that health systems support women living with HIV to realize their full right to health, including sexual and reproductive health and rights, bodily autonomy and rights to informed consent.
"This report issues a powerful call to action to put the autonomy, desires and needs of women living with HIV at the centre of their sexual and reproductive health care programmes." said Immaculate Owomugisha Bazare, Global Coercion Scan Committee, ICW Global Steering Committee Member.
Background
The Confronting Coercion report was developed through a blend of qualitative and quantitative research, incorporating insights from a gendered analysis of recent Stigma Index 2.0 data, a desk review of literature, and a qualitative study involving women, trans and gender non-binary people living with HIV who shared experiences of reproductive coercion over the past 3 years. The qualitative part of the study looked at coercion, mistreatment and neglect related to the SRHR of women and gender diverse people living with HIV in HIV, SRH and maternity care settings.
UNAIDS has supported the development of the report to address systematic gender inequalities, in particular gender-based discrimination and violence against women living with HIV, which fuels the HIV epidemic.





Feature Story
A transformative journey: Parisa's decades-long battle against HIV stigma and discrimination
18 July 2024
18 July 2024 18 July 2024Every pain yields a lesson, and every lesson transforms a person
Parisa's life was forever altered by HIV 25 years ago. The virus struck her family, snatching her husband's job and halting her child's education. Tragically, her husband passed away two years later, leaving Parisa to navigate the daunting landscape of loss and discrimination.
“I did not have a clue about this illness. It was, in fact, the first time I had even heard the word 'AIDS'”.
Undeterred by adversity, Parisa embarked on a relentless mission for human rights, determined to combat the pervasive stigma and discrimination surrounding HIV. Initially, she immersed herself in seminars and conferences, volunteering tirelessly at counselling centres, where she shared her own experiences to chip away at the stigma and discrimination.
“My activities in the Positive Club allowed me to broaden my knowledge and take more effective steps toward raising public awareness, reducing HIV stigma and discrimination, and helping my peers… IRCHA and UNAIDS supported me to expand my knowledge and gave me the chance to exchange my experiences with the members of Positive Clubs in and out of the country.”
Her unwavering dedication caught the attention of Dr Minoo Mohraz, the former director of the Iranian Research Centre for HIV/AIDS (IRCHA), who offered her a pivotal role in a Positive Club—a sanctuary for those grappling with similar challenges. Thus began Parisa's transformative journey, marked by a series of initiatives aimed at raising awareness, eradicating stigma and discrimination, and supporting her peers.
WHAT IS THE POSITIVE CLUB INITIATIVE? The Positive Club is a meeting place for people living with HIV, who run the club themselves, with supervision from Parisa and colleagues. At the club, people receive training in arts, and sports, and as peer educators. The Positive Club initiative was one of the successful programmes aimed at promoting positive health, dignity, and HIV prevention; it has been running for over 12 years with support from UNAIDS in collaboration with national partners and civil society organizations. Through this initiative, over 10,000 people living with HIV have been supported across 25 Positive Clubs, empowering them through training classes, workshops on HIV prevention, care and treatment, counselling sessions, and psychosocial support.
Over the years, Parisa's efforts have been nothing short of extraordinary. From managing a Positive Club in Tehran to representing people living with HIV in various influential platforms, including Iran's Country Coordinating Mechanism, its Oversight Committee, and Global Fund, she has been a relentless advocate for change.
Her initiatives have spanned diverse arenas, from radio shows and collaborations with filmmakers to training workshops for religious leaders and healthcare providers. Parisa's impact reverberates across borders, as she leverages regional platforms like MENA Rosa --the first regional network dedicated to women living with HIV in the Middle East and North Africa-- to exchange experiences and champion global efforts against HIV stigma and discrimination with a particular focus on Women living with and affected by HIV.
Amid the COVID-19 pandemic, Parisa's compassion for people living with and affected by HIV was once again evident. She mobilized support networks to provide essential supplies for Positive Club members and vulnerable families, ensuring that the crisis does not exacerbate the challenges faced by PLHIV.
Reflecting on the progress made over the last 25 years, Parisa acknowledged the remarkable strides in combating HIV-related stigma and discrimination. Efforts to eliminate HIV-related stigma and discrimination have been led by the UNAIDS Country Office for Iran, alongside national partners of the AIDS Control Programme. Notably, the first PLHIV Stigma Index study, conducted in 2010, laid the foundation for understanding the landscape of stigma in Iran. Subsequently, a second PLHIV Stigma Index study, was carried out by the network of PLHIV in collaboration with UNAIDS, Global Network of PLHIV (GNP+), International Community of Women Living with HIV (ICW), Johns Hopkins Medical University (JHMU), National AIDS Programme (NAP), and with financial support from Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria (GFATM) /UNDP. Parisa played an important role in implementing the Stigma Index 2.0 which provided updated insights.
COMPARING OF BOTH OF IRAN’S STIGMA INDEX STUDIES A comparison between the two Stigma Index studies conducted ten years apart, using updated methodologies, revealed promising changes. The prevalence of self-stigma among PLHIV decreased significantly from 80% to 40%. Similarly, the percentage of PLHIV refraining from seeking medical help has decreased from 80% to 19%, underscoring improved accessibility to healthcare services and increased health-seeking behaviour among affected individuals. Overall, reports of stigma and discrimination have decreased from 71% to 47%, reflecting tangible improvements in societal attitudes to HIV.
Parisa reflects on these notable shifts in HIV-related Stigma observed between the two studies. In the initial Stigma Index conducted a decade ago, internal stigma was predominant among PLHIV, followed by societal and healthcare provider stigma. However, in the subsequent study, internal stigma was significantly reduced, while stigma and discrimination from healthcare providers emerged as the most prevalent issue. The improvement observed in internal stigma among PLHIV could be partly attributed to the work of the empowering Positive Clubs. Additionally, this improvement highlights the importance of ongoing efforts to address stigma and discrimination comprehensively, with a particular focus on healthcare settings. By acknowledging these shifts and persisting in their efforts, UNAIDS Iran, Parisa and her colleagues remain committed to building a future free from the burdens of HIV-related stigma and discrimination.
Through her nearly two decades of hotline counselling experience, Parisa has witnessed a shift in attitudes, with increased awareness and openness surrounding HIV discourse.
She credits grassroots campaigns and community-led initiatives for driving this transformation, paving the way for a more inclusive society.
“Positive Clubs have been played a very effective role in empowerment and phycological support to the members and reducing stigma and discrimination.”
In 2019, Iran joined the Global Partnership to Eliminate all forms of HIV-related stigma and discrimination, prioritizing a strong emphasis on interventions within communities, emergency/humanitarian settings, and healthcare facilities. With support from UNAIDS, protocols and training packages were developed to address stigma and discrimination in these critical areas. These efforts were carried out in close collaboration with national partners and civil society organizations, with training workshops being a key component of the initiative.
OVERVIEW OF GLOBAL PARTNERSHIP The Global Partnership for action to eliminate all forms of HIV-related stigma and discrimination is a critical vehicle for action to mobilise all countries to reach the political declaration and Global AIDS Strategy targets. It leverages partnerships to enhance coordination of interventions and funding; it provides knowledge and evidence-guided technical support; and increases accountability mechanisms and community leadership.
Parisa was actively involved in the implementation phase of these projects. Her contributions have been instrumental in advancing the work to eradicate HIV-related stigma and discrimination across humanitarian, healthcare, and community settings.
However, Parisa acknowledges the persistent challenges faced by PLHIV, from sporadic bouts of self-doubt to occasional rejections and the lingering shadows of depression and fear. Despite these hurdles, she remains steadfast in her belief that we can achieve a future free from stigma and discrimination.
As Parisa continues her tireless advocacy, her journey stands as a testament to the resilience of the human spirit and the power of collective action in fostering a world where every individual, regardless of their HIV status, is embraced with dignity and compassion.
“Of course, people living with HIV still experience stigma and discrimination at different stages of their lives but have a hope for a day free of stigma and discrimination.”
UNAIDS has played a pivotal role in the establishment and sustained operation of Positive Clubs for over a decade, catalyzing transformative changes in the lives of people living with HIV such as Parisa and in the fight against stigma and discrimination. Nonetheless, the journey towards eliminating stigma and discrimination remains unfinished, albeit considerably smoother and more steadfast with the collaborative efforts and political commitment of initiatives such as the Global Partnership.
“Together, we continue to pave the way towards a future free from the burdens of stigma and discrimination for all individuals living with and affected by HIV.”




Feature Story
Girls’ education for HIV prevention at 1st Pan-African Conference on Girls’ and Women’s Education in Africa
08 July 2024
08 July 2024 08 July 2024Girls’ education as a tool to prevent HIV infection has been centered at the 1st African Union Pan-African Conference on Girls’ and Women’s Education in Africa. This followed African leaders designating education as the 2024 African Union theme of the year.
At a high-level side event hosted by the Education Plus Initiative on the first day of conference held at the African Union Commission in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, leaders, girls’ and women’s networks and advocates called for greater investments in girls’ education.
“Some people claim that providing girls with secondary education is too expensive. Such claims fail to consider the exponentially higher cost of not educating them,” said UNAIDS Executive Director, Winnie Byanyima. “We can get all our girls and boys to complete secondary education; that should be our legacy."
UNICEF calculates that 34 million girls in sub-Saharan Africa are out of secondary school. According to the Global Education Monitoring (GEM) Report 2023, in all regions in Africa, there are more girls out of school at the secondary level than boys, with gender disparities worsening as children move up to higher levels of education in favour of boys over girls. In sub-Saharan Africa, less than half of adolescent girls complete secondary education, their percentage standing at 42% and there has been no progress at all in closing this gap in the past 20 years. Sub-Saharan Africa is the region furthest from parity at the expense of girls, with no progress since 2011 at the lower secondary level and since 2014 in upper secondary.
Gender is a key factor linked to disparities in enrolment, retention, completion, and learning outcomes through social conditioning, gender-based differences in parental expectations and education-related investments, child marriages and early childbearing, female genital mutilation, child labour, gender-based violence, period poverty and discrimination.
More than forty years into the HIV response, Africa remains an epicenter of the AIDS epidemic with adolescent girls and young women being disproportionately affected. Every week 3100 adolescent girls and young women acquired HIV in sub-Saharan Africa. Every three minutes, an adolescent girl or young woman aged 15-24 years acquired HIV in 2022 in sub-Saharan Africa. Adolescent girls and young women aged 15-24 years in the region were more than three times as likely to acquire HIV than their male peers in 2022.
UN agencies, African Union representatives, government ministers, and young women leaders called for accelerated actions to translate commitments to action through leveraging girls' education for gender equality and preventing HIV, child marriage, teenage pregnancies, violence, gender-related stigma and discrimination in Africa.
Speakers emphasized the connection between health and education. Ministers spoke about key policy reforms and best practices aimed at promoting girls' education, including creating safe and inclusive school environments, strategies to get girls into secondary school, and the readmission policy that addresses high dropout rates due to pregnancy. UN co-leads emphasised the need for improved collection of data disaggregated by sex and other relevant population characteristics to better understand educational participation, progression, and learning, and using gender-sensitive data for policymaking and planning.
Other issues highlighted included the integration of digital literacy programs into the secondary education and vocational training curriculum to facilitate smooth transitions from school to employment; integrate gender equality into all aspects of the education system, including curriculum-based comprehensive sexuality education and life skills, address gender-based violence within schools and discriminatory laws and practices, and access to information, non-discriminatory HIV and sexual and reproductive health services access.
Young women leaders spoke on the role of partnerships and young women's leadership. Participants highlighted the upcoming 30th anniversary of the Beijing Declaration as an opportunity moment to accelerate accountability and commitments, as well as the CSW Resolution 60/2, Women, the Girl Child and HIV and AIDS as significant mechanisms to address political and resource gaps so no woman or girl is behind in the HIV response.
Education Plus is a rights-based, gender-responsive action agenda to ensure adolescent girls and young women have equal access to quality secondary education, alongside key education and health services and support for their economic autonomy and empowerment. Co-led by five UN agencies, the initiative builds on existing frameworks like the Transforming Education Summit, the Continental Education Strategy for Africa (CESA) and the Dakar Education for All (EFA) Declaration to push for access and completion of education for women and girls in Africa.
Quotes
" Some people claim that providing girls with secondary education is too expensive. Such claims fail to consider the exponentially higher cost of not educating them. We know the consequences when girls can’t finish secondary school: higher risks of sexual violence, early marriage, unwanted pregnancy, complications in pregnancy and childbirth, and HIV infection. But when a girl completes secondary school, it helps her to be safe and strong. If all girls complete secondary education, adolescent pregnancy could be cut by 75% and early marriage could be virtually eliminated. An extra year of secondary school can increase women’s eventual wages by 15-25%. We can get all our girls and boys to complete secondary education; that should be our legacy."
We must recognize the intersecting challenges girls face, including HIV. They face extraordinarily high levels of HIV infections. Women and girls represented 63% of all new HIV infections in Africa in 2022. Empowering girls with knowledge is key to ending AIDS as a public health threat. Education is the best HIV prevention tool available.”
“African nations should ensure that young people not only gain vital knowledge but also acquire life skills, values, attitudes, and make decisions in order to live healthy and fulfilled lives. Through the AU strategy, we will see increased awareness about the importance of investing in education and the health of children and adolescents.”
“Girls’ education is not only a right, but will also result in broad socio-economic development for countries. We are creating a safe and conducive environment for adolescent girls and young through the criminalization of child marriage, FGM, school-related gender-based violence, and sexual harassment, particularly sexual exploitation perpetrated by teachers. We provide life skills and comprehensive sexuality education in schools and ensure an inclusive school environment for children with disabilities, with specific attention to girls. We have enhanced social protection strategies, including cash transfers to poor households to ensure that girls go to school and are not engaged in care work and child labour.”
“Girls who dropped out due to early pregnancies or early unwanted pregnancies are readmitted. We have a national girls’ education strategy aimed at facilitating the pace at which Malawi may achieve sustainable development goals. We emphasize universal primary education, the promotion of gender equality and empowering women.”
“We are trying to remove the cultural norm barriers and negative gender stereotypes that contribute to gender-based violence and discrimination against adolescent girls and young women with a male engagement strategy. Inclusive education provides special provisions for the less privileged and disadvantaged children and youth; user-friendly infrastructure, teaching and learning materials and provision of expert teachers.”
“Education is a human right. The Education Plus Initiative is driving policy changes in Africa. Education Plus seeks to keep adolescent girls and young women in school by simply unequivocally saying no to child marriage, no to violence, no to HIV infections, no to gender-related stigma, and of course, no to harmful practices. We want to keep girls in secondary education and make sure they stay there and complete their education. We do that by supporting sexual and reproductive health and rights, comprehensive sexuality education and work for integration HIV awareness, preventing and managing learners pregnancies and addressing school-related gender-based violence.”
“We need to scale up effective interventions to increase HIV knowledge and transform gender norms, and hence girls’ access to services. We should explore the potential of innovative solutions offered by digital technologies to mobilize and provide young women and adolescent girls with comprehensive HIV information. Let's do more, particularly for those girls living with HIV to be meaningfully engaged in the HIV response. Young women must have a formal seat and a safe space to raise their needs. let's move from rhetoric to action.”
“The numbers are unfortunately very clear: highest adolescent pregnancy rates of the world are in sub-Saharan Africa, highest percentages of women first married or in union before 18, young women more than 3 times as likely of HIV infection, or unacceptably high rates of justification of wife beating among adolescents. Fortunately, we benefit from a strong set of political commitments and strategies to face these issues. There is the Education Plus Initiative, the WCA Commitment for Educated, Healthy and Thriving Adolescents and Young People, the ESA Commitment, and the AU Continental Strategy on Education for Health and Wellbeing of Young People in Africa. It is high time to convert the commitments and strategies in concrete results for adolescent girls and young women.”
“Girls need an affirming environment. Where there's ignorance, there's a lot of resistance to education and sexuality education in the curriculum. We need to engage to change the environment, talking with parents, men and boys, community members and leaders for them to have access to information because they have a great influence on the lives of these young people. We need inclusive advocacy, especially the rural grassroots and true localization of information and interventions.”
Our work
Related


Feature Story
United Nations General Assembly debate highlights the need for urgent action to ensure that progress in the HIV response is accelerated and sustained
26 June 2024
26 June 2024 26 June 2024On 19 June 2024, the United Nations General Assembly convened to evaluate the progress made in the response to the AIDS epidemic. The yearly session provided a platform for Member States to reflect on achievements, confront persistent barriers, and chart a course forward towards ending AIDS by 2030. The UN Secretary-General’s progress report formed the basis of the debate.
Member States celebrated the significant achievements towards ending AIDS, while highlighting ongoing challenges that must be overcome to reach the promise of ending AIDS as a public health threat by 2030.
The commitment to the 95-95-95 targets and the progress made in eliminating vertical transmission of HIV, especially through the use of decentralized community-based services, were highlighted as pivotal to the success of the HIV response.
Many member states stressed the crucial role that promoting a human rights-centered approach has had in the fight against HIV. They highlighted the significance of comprehensive multi-sectoral responses, including education on sexuality and robust support for sexual and reproductive health and rights. They pointed to the harm of actions that undermine gender equality and LGBTQI+ rights. They emphasized the shared duty of every country to protect everyone’s human rights.
The need for continued global solidarity and enhanced multilateral cooperation was emphasized as key to tackling the remaining challenges. Calls for increased domestic and international funding were echoed, noting that sustained investment is crucial to maintaining progress and for expanding access to innovative prevention and treatment options.
The UN General Assembly annual review served as a poignant reminder of the collective responsibility to uphold the rights and dignity of all people affected by HIV.
Inspired by the lessons learnt from the AIDS response, the upcoming Summit of the Future scheduled for September 2024 will explore how common challenges can be overcome.
Against a backdrop of geopolitical shifts and economic uncertainties, the HIV response serves as a beacon of how multilateral solidarity saves and transforms lives.